Fig. 2.
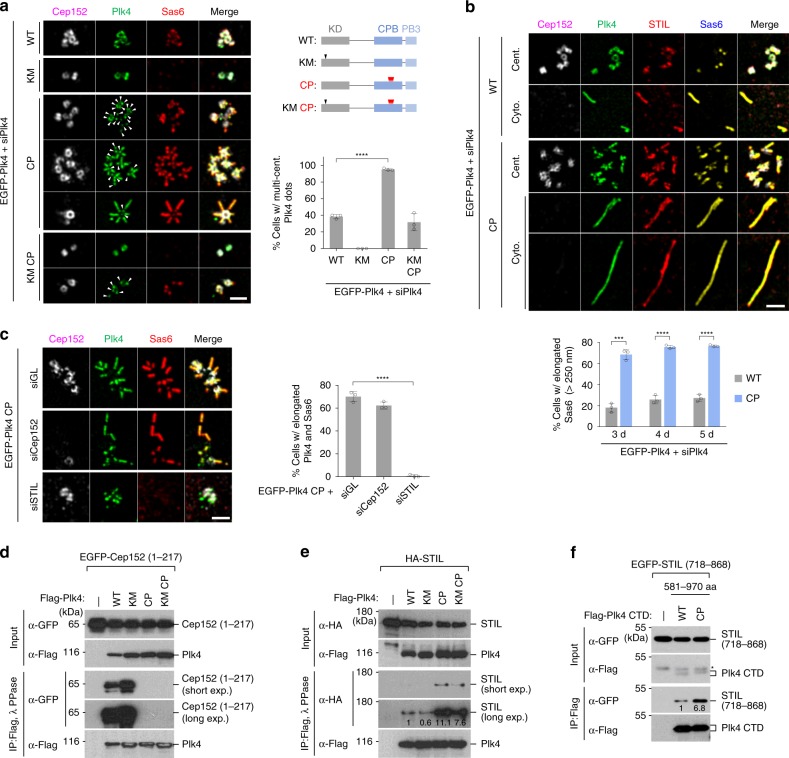
A condensation-proficient Plk4 CP mutant drives procentriole formation by switching its interaction from Cep152 to STIL. a, b 3D-SIM analysis of immunostained U2OS cells stably expressing the indicated EGFP-Plk4 constructs under Plk4 RNAi (siPlk4) conditions. Bar, 1 μm. Quantification of images is shown in mean ± s.d. (n = 3 independent experiments). Arrowheads in a, dot-state Plk4 signals; schematic diagram in a shows the sites of the KM and the quadruple CP mutations. Elongated procentrioles in both centrosome (cent.) and cytosol (cyto.; as judged by the absence of the centrosomal Cep152 signal) are shown in b. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (unpaired two-tailed t test). c 3D-SIM analysis of immunostained U2OS cells stably expressing the EGFP-Plk4 CP mutant under various RNAi conditions. Bar, 1 μm. Quantified data are shown in mean ± s.d. (n = 3 independent experiments). ****P < 0.0001 (unpaired two-tailed t test). d–f Immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting analyses using HEK293T cells cotransfected with the indicated constructs. IP samples were then treated with λ phosphatase (PPase), where indicated, to convert phosphorylated, slow-migrating forms into a fast-migrating form, and then separated by 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) for immunoblotting. Numbers denote relative signal intensities. Asterisk denotes remnants of STIL signals from a prior anti-GFP blotting. Source data are provided as a Source Data file for a–c