Fig. 7.
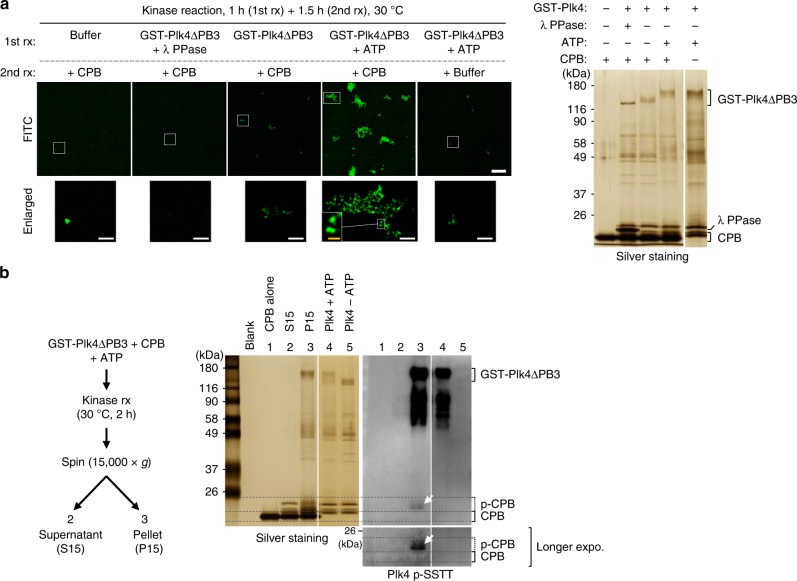
Phosphorylation of CPB by Plk4 induces clustering in vitro. a 3D-SIM images showing CPB condensates generated by GST-Plk4∆PB3-dependent phosphorylation in vitro. Bar, 10 μm. Dotted boxes, areas of enlargement (bar, 2 μm). Yellow bar in the dotted box, 0.5 μm. Kinase reactions were carried out in two steps—Plk4∆PB3 activation step (1st rx) and CPB phosphorylation step (2nd rx). Reaction products were decorated with FITC to visualize CPB condensates and imaged (left). The same reaction products were separated by 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) for silver staining (right). Note that FITC-decorated condensates contributed by GST-Plk4∆PB3 (5th panel) are negligible. b Immunoblotting analysis showing Plk4∆PB3-phosphorylated CPB generates pelletable condensates in vitro. Following a kinase reaction, a sample was fractionated into supernatant (S15) and pellet (P15), and then separated by 8% SDS-PAGE. Note that Plk4∆PB3-reacted PC3-phosphorylated CPB (α-pSSTT panel) is present only in the P15 fraction (arrow)