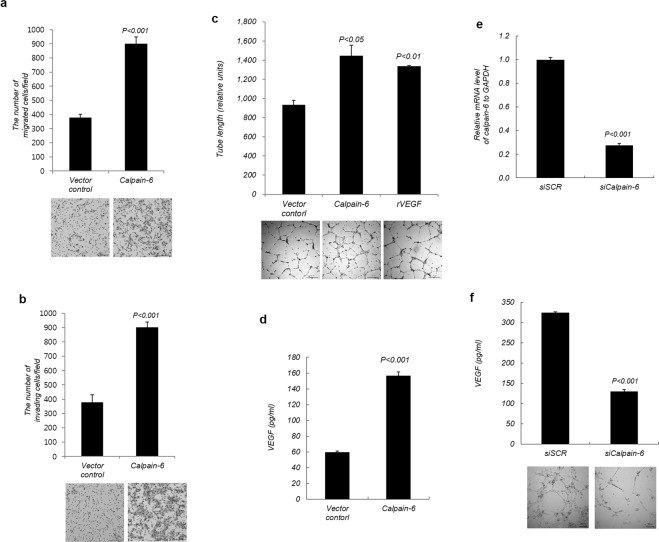
Figure 3.
Calpain-6 promotes angiogenesis in vitro. (a,b) Secreted VEGF by calpain-6 increased HUVEC migration and invasion. HUVECs seeded on Transwells for the migration assays (a) or on Matrigel-coated Transwells for the invasion assays (b) were co-cultured with stable calpain-6-overexpressing or control vector HEK293 cells for 3 h. The number of migrated or invaded cells was photographed under a light microscope, and mean values were determined. (c) Calpain-6 overexpression in HUVECs promotes tube formation in vitro. Tube formation assays were performed with HUVECs transfected with control vector or calpain-6 expressing vector. As a positive control, HUVECs were incubated with recombinant human VEGF (10 ng/mL). The formation of tubular structures was captured by an inverted light microscope, and tube lengths were quantified by Inform. (d) Calpain-6 expression increased VEGF secretion in HUVECs transected with a calpain-6 expressing vector. VEGF protein in the conditioned medium of HUVECs transfected with control vector or calpain-6 expressing vector was analyzed by ELISA and the results were expressed as mean VEGF produced in the conditioned medium. Data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (e) Silencing of calpain-6 expression by siRNA. Calpain-6 stable HEK 293 cells were transfected with scrambled (SCR) and calpain-6 siRNA, respectively, and then analyzed the relative calpain-6 mRNA expression by real-time PCR. The results were expressed as the mean values. (f) Silencing of calpain-6 by siRNA decreased the VEGF secretion in HEK293 cells and leads to reduction in tube formation in HUVECs. The quantitation of VEGF secreted in the CM of stable HEK293-calpain-6 cells by calpain-6 siRNA was analyzed by ELISA and the results are expressed as mean VEGF produced in the conditioned medium. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.