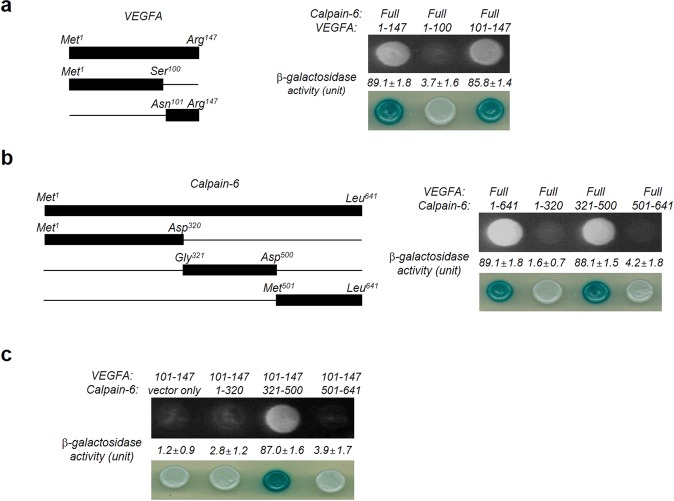
Figure 4.
Domain mapping analysis of the VEGFA–calpain-6 interaction using the yeast two-hybrid assay. (a) The left panel is a schematic diagram showing the respective cDNA constructs for the VEGFA full-length and deletion mutants constructed by standard cloning and then verified by DNA sequencing. In the right panel, yeast transformants were assayed for their ability to grow on medium lacking leucine (upper panel) and for galactosidase expression through the formation of a blue colony on the plate containing X-gal (bottom panel). The values of β-galactosidase activity (unit), examined by adding o-nitrophenyl β-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) agents, are indicated below their corresponding lanes. The data represent three independent experiments and are shown as means ± SD. (b) Identification of the interacting domains between calpain-6 and VEGFA through a yeast two-hybrid analysis. The left panel displays a schematic representation of the cDNA constructs for the full-length and truncated mutant calpain-6 fusion proteins. The right panel shows the results of the protein–protein interactions assessed in the yeast two-hybrid assay. The yeast transformants were assayed for their ability to grow on medium lacking leucine (upper panel) and for galactosidase expression through the formation of a blue colony on a plate containing X-gal (bottom panel). (c) Biological interactions between the cDNA constructs for VEGFA (Asn101–Arg147) and three calpain-6 deletion proteins (Met1–Asp320, Gly321–Asp500, Met501–Leu641), as determined by the yeast two-hybrid analysis. The C-terminal of VEGFA interacted with the domain comprising the amino acid region 321–500 in calpain-6.