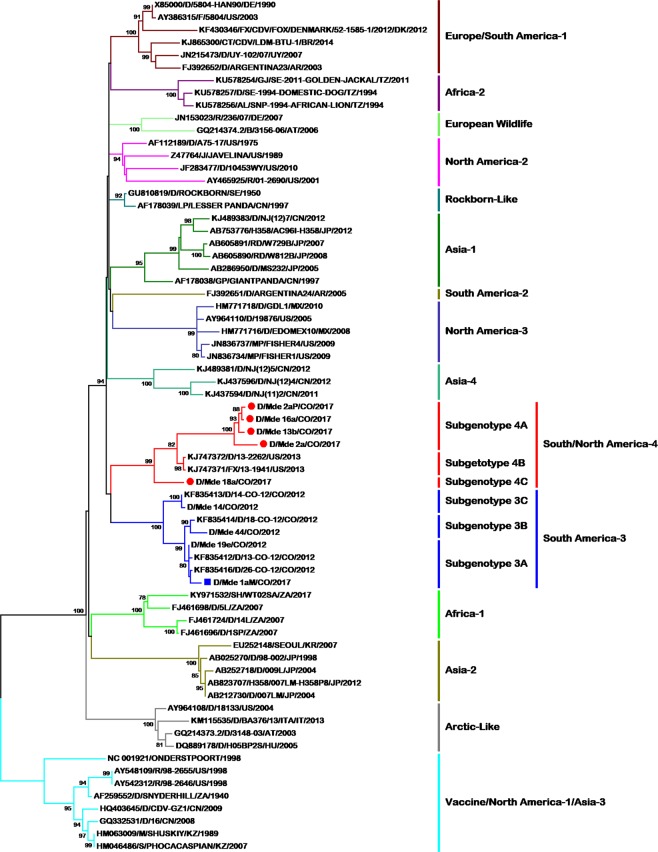
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationships between 68 CDV strains based on H gene sequences. The phylogenetic tree was inferred by the maximum likelihood method using 1000 replicates. GenBank accession numbers, the species from which each isolate was obtained, name of the strain, country of origin, and year of isolation are indicated in the tip labels if available. Numbers at the nodes are bootstrap values for the clade. Abbreviations for animal species: AL: African lion (Panthera leo), B: badger (Meles meles), CT: Cerdocyon thous, D: dog (Canis lupus familiaris), F: ferret (Mustela putorius furo), FX: fox (Vulpes urocyon), GJ: golden jackal (Canis aureus), GP: giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca), J: javelina (Tayassu pecari), LP: lesser panda (Ailurus fulgens), M: mink (Neovison vison), MP: Martes pennanti, R: raccoon (Procyon lotor), RD: raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides), S: seal (Phoca vitulina), SH: spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta). H358: human lung cells. Abbreviations for countries: AR: Argentina, AT: Austria, BR: Brazil, CN: China, CO: Colombia, DE: Germany, DK: Denmark, HU: Hungary, IT: Italy, JP: Japan, KR: South Korea, KZ: Kazakhstan, MX: Mexico, SE: Sweden, TZ: Tanzania, US: United States, UY: Uruguay, ZA: South Africa.