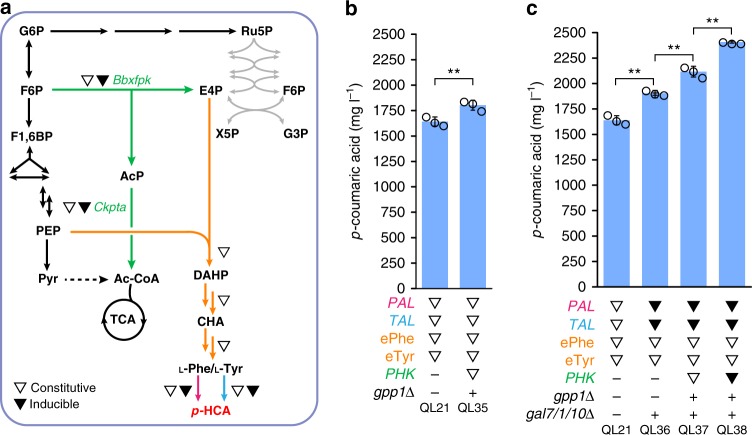
Fig. 4.
Employment of a combinatorial strategy to increase the production of p-HCA. a Schematic overview of the metabolic pathway for p-HCA production with an improved supply of precursor E4P and dynamic control over the relevant biosynthetic genes, as indicated by triangle symbols: open triangles indicate the use of constitutive strong promoters to control gene expression, while filled triangles indicate the use of galactose-inducible promoters. See Fig. 1 legend regarding abbreviations of metabolites and Fig. 3 legend for gene details. b Integration of the PHK pathway with combined ePhe-PAL and eTyr-TAL branches leads to increased p-HCA production. eTyr refers to enhanced tyrosine biosynthesis mediated through the beneficial effect of MtPDH1. c Dynamic control of biosynthetic genes via use of the GALp-controlled expression system significantly increases p-HCA production. Cells were grown in defined minimal medium with six tablets of FeedBeads as the sole carbon source and 1% galactose as the inducer when required. Cultures were sampled after 96 h of growth for p-HCA detection. Statistical analysis was performed by using Student’s t test (one-tailed; two-sample unequal variance; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). All data represent the mean of n = 3 biologically independent samples and error bars show standard deviation. The source data of figures b and c are provided in a Source Data file