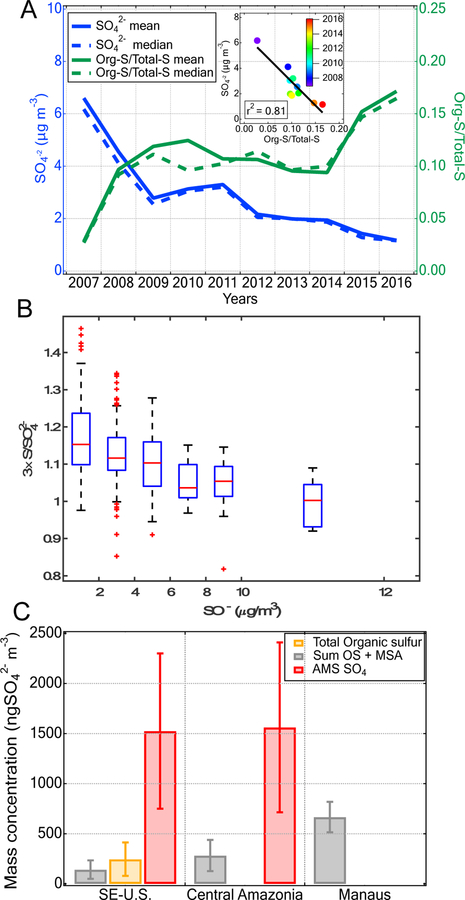
Figure 2.
(A) Correlation between total sulfate and organosulfur fraction and (B) Evolution of organosulfur fraction as a function of Sulfinorg at the Great Smoky Mountain Site (Look Rock, TN) during summer (May – September) from 2007–2016, using the National Park Service IMPROVE PM2.5 database. If particulate organosulfur compounds are not present, the sulfate (SO42−) mass measured by IC should equal three times the sulfur mass concentration measured by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), since the molar mass of sulfur and sulfate are 32 and 96 g/mol, respectively. A value of 3×S/ SO42− lower than 1 is caused by the limitation of the analytical techniques to differentiate 3×sulfur from SO42−.42 (C) Average mass concentration of the identified organosulfates + methane sulfonic acid (OS + MSA) and total organosulfur compounds (Org-S) in the PM2.5 samples collected during the 2013 SOAS campaign as well as the average mass concentrations of the sum of OS + MSA quantified in downwind Manaus and Manaus. AMS data from SE-U.S. and downwind Manaus are also presented.