Figure 4.
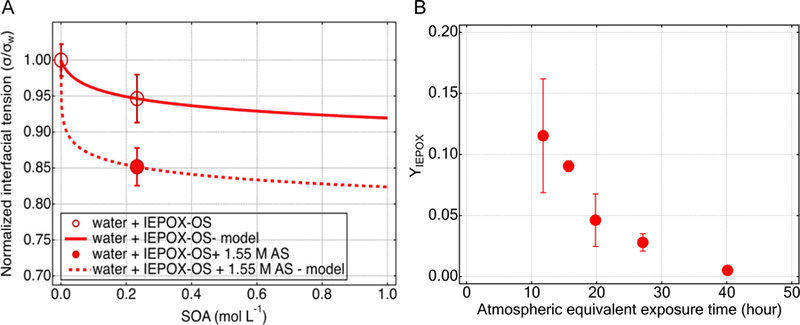
(A) Measured and modeled interfacial tension (IFT) of IEPOX-OS. Microfluidic measurements of IFT (circles); two parameter model treatment of SOA in pure water (solid line), using a binary model 63,100 ; and model treatment of SOA in ammonium sulfate (AS) solution (dashed line), using an adapted form of the binary model adapted for salt-containing organic aqueous solutions that includes known organic model parameters from the solid line and the Setschenow constant as the single adjustable model parameter (dashed line). (B) IEPOX reactive uptake coefficient (γIEPOX), obtained from flow tube experiments performed at the University of Washington, on aqueous ammonium bisulfate particles as a function of atmospheric equivalent exposure time defined as the length of the time that an aerosol is exposed to IEPOX gases, assuming gas-phase IEPOX concentration of 1 ppb and an aerosol surface area density of 300 μm2 cm−3. The atmospheric equivalent exposure time is obtained from the experimental reaction time by multiplying the ratio of experimental-to-ambient concentration of IEPOX (=75) represents an upper limit.
