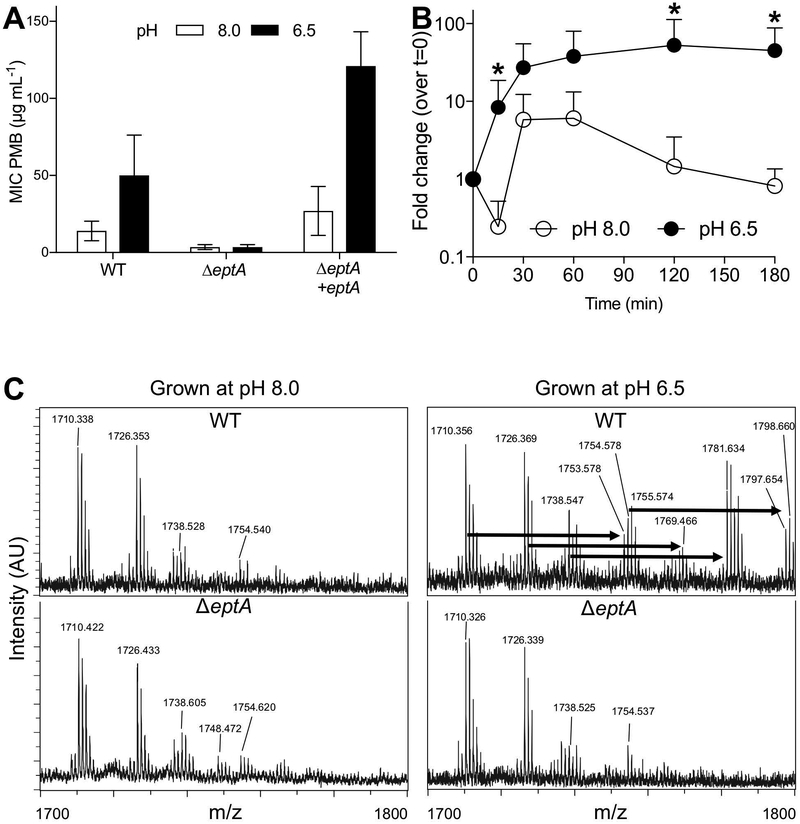
Figure 3.
The eptA homolog of V. fischeri (VF_A0210) is differentially expressed under acidic conditions and acts as a lipid A ethanolamine transferase. (A) pH-dependency of PMB MIC assay performed on wild-type V. fischeri ES114 (WT) and its derivatives, with or without the eptA gene. Bars represent mean with 95% confidence intervals (CI). (B) Transcription of eptA over time after exposure to acidic or basic pH. Points represent mean + SD. Data represent at least three biological replicates, *: p≤0.1 according to Mann-Whitney test. (C) Representative mass spectrometry spectra of lipid A extracts isolated from either wild-type V. fischeri or its ΔeptA derivative, grown at pH 6.5 or 8.0. Arrows indicate 43 m/z shifts, consistent with a dehydration addition of an ethanolamine residue.