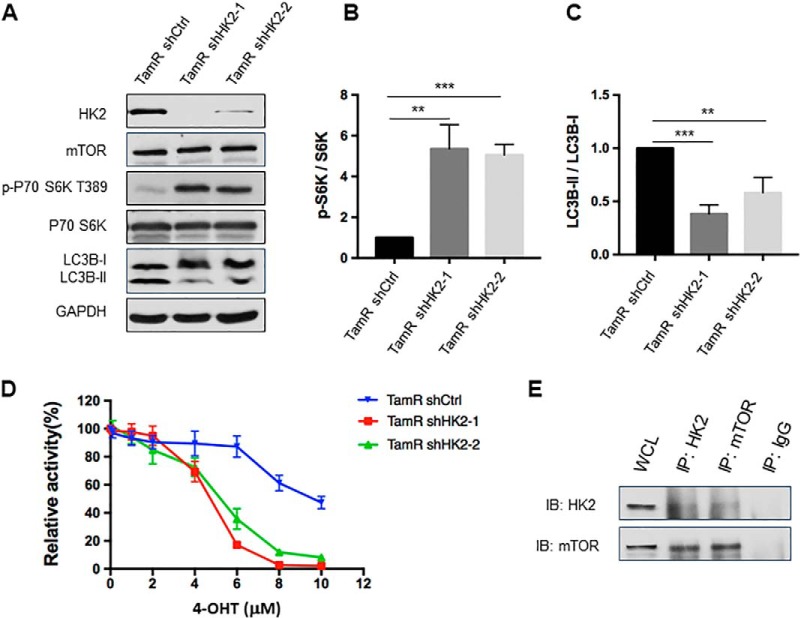
Fig. 6.
Genetic depletion of HK2 led to increased mTOR activity and attenuated autophagy, and re-sensitized tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells to 4-OHT. A, Validation of HK2 and mTOR expression levels and phospho-S6K, LC3B-II/LC3B-I changes after knocking down HK2 in TamR MCF-7 cells with two different sequences of shRNA. B, C, Quantification of changes in p-S6K and LC3B-II/LC3B-I in TamR MCF-7 cells upon shRNA-mediated knockdown of HK2. The values for p-S6K and LC3B-II were normalized against the band intensities of S6K and LC3B-I, respectively, The data were presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). The p values were calculated using unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test: **, 0.001 ≤ p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. D, TamR MCF-7 shHK2 stable knockdown cells were treated with serially diluted 4-OHT for 72 h and cell viability was measured using CCK8. The data were normalized to control groups (ethanol) and represented by the mean and S.D. of results from three independent measurements. E, TamR MCF-7 cells were collected and cell lysates were immuno-precipitated using an antibody for either HK2 or mTOR, and the captured proteins were eluted and Western blotting was employed to monitor the interaction between HK2 and mTOR.