Fig. 1.
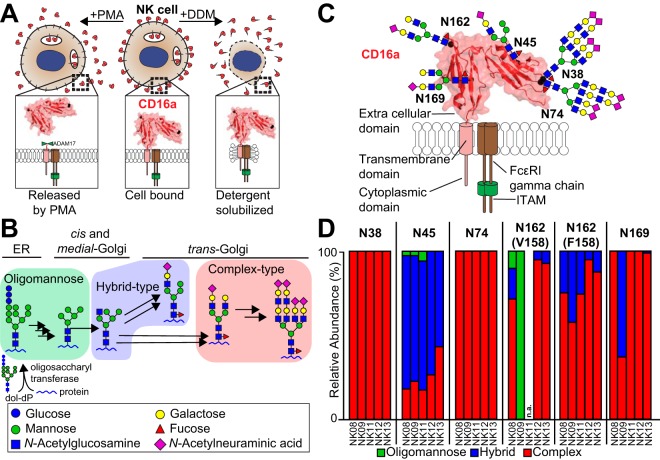
CD16a is the primary Fc γ receptor expressed on NK cells and is heavily modified with N-glycans. A, CD16a was isolated by either NK cell stimulation with PMA to release CD16a or by lysing the cell with detergent (DDM). B, An abbreviated representation of the N-glycan remodeling pathway in mammals is shown that generates a diverse repertoire of modifications. C, A cartoon of CD16a topology shows the extracellular, transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains as well as the most abundant N-glycans at the five sites, scaled to the size of the protein. D, The relative abundance of the three N-glycan types identified at each CD16a site from each of five donors (donor identifier is listed below the bar and N-glycosylation site above). Peptides containing N162 glycosylation also reveal donor allotype (V158 v. F158) and are reported separately. n.a., not applicable. See also supplemental Tables S1–S2 and supplemental Figs. S1 and S2.