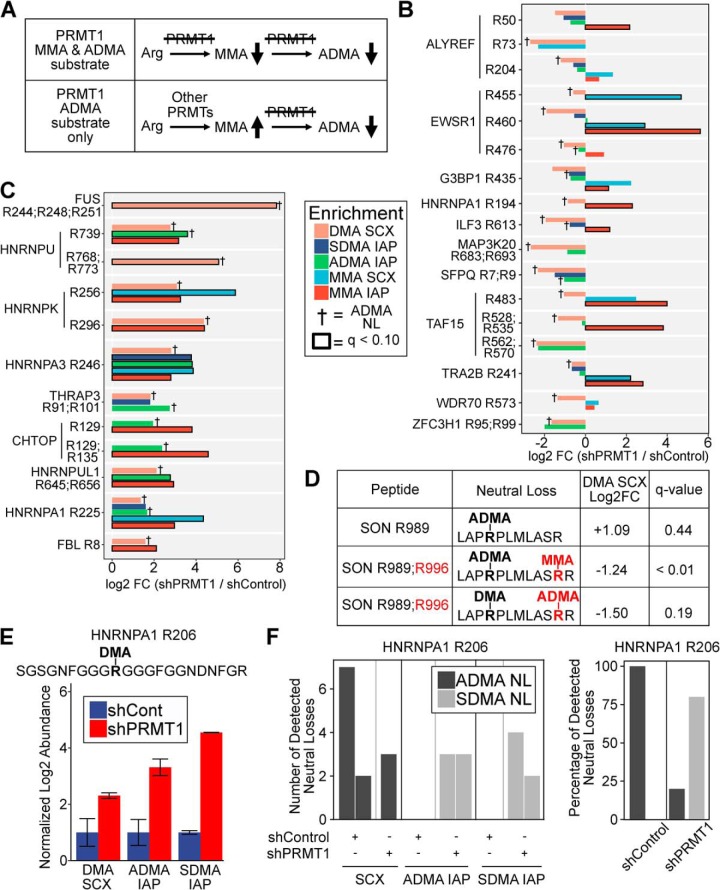
Fig. 6.
Integrated analysis of methyl-arginine forms reveals novel PRMT1 substrates and ADMA substrate scavenging. A, Schematic depicting the expected trends in MMA and ADMA levels for methylation sites targeted by PRMT1 for both MMA and ADMA methylation (top) and ADMA but not MMA methylation (bottom). B, Integrated analysis of MMA and ADMA levels revealed novel PRMT1 substrates. Log2 fold change of methylation levels for shPRMT1 cells compared with shControl cells are shown for different methyl peptide enrichment protocols: DMA peptides identified by SCX, SDMA IAP, ADMA IAP, MMA peptides identified by SCX, and MMA IAP. Peptides were selected based on decreased ADMA levels in one or more experiments, and the presence of MMA data for the same methylation site. † denotes methyl peptides with confirmed ADMA neutral loss. Bold outline indicates methyl peptides with FDR q-value < 0.1 by permutation t test in Perseus. C, Integrated analysis of MMA and ADMA levels revealed substrate scavenging in the absence of PRMT1 activity. Log2 fold change of methylation levels for shPRMT1 cells compared with shControl cells are shown for different methyl peptide enrichment protocols: DMA peptides identified by SCX, SDMA IAP, ADMA IAP, MMA peptides identified by SCX, and MMA IAP. Peptides were selected based on increased ADMA levels in one or more experiments, and the presence of MMA data for the same methylation site. † denotes methyl peptides with confirmed ADMA neutral loss. Bold outline indicates methyl peptides with FDR q-value < 0.1 by permutation t test in Perseus. D, Identification of SON R996 as a PRMT1 substrate. A peptide with neutral loss confirmed ADMA R989 was upregulated upon PRMT1 knockdown. A peptide with neutral loss confirmed ADMA R989 and MMA R996 was downregulated significantly in the mixed SCX data seet. A peptide with DMA R989, neutral loss confirmed ADMA R996, and a missed cleavage at R996 was downregulated upon PRMT1 knockdown. This suggests that PRMT1 knockdown reduced ADMA R996 and MMA R996, allowing tryptic cleavage, thereby resulting in increased levels of the fully cleaved tryptic peptide with ADMA R989. E–F, HNRNPA1 R206 exists in both ADMA and SDMA modified form and may switch from ADMA to SDMA upon PRMT1 knockdown. (E) The methyl peptide SGSGNFGGGRGGGFGGNDNFGR (DMA site underlined and italicized) was upregulated in SCX, ADMA IAP, and SDMA IAP. The log2 fold change of shPRMT1 cells compared with shControl cells is shown, normalized to shControl. F, Analysis of neutral loss ions demonstrated that ADMA neutral losses were primarily identified in shControl cells, whereas SDMA neutral losses were primarily identified in shPRMT1 cells. (left) Each bar represents a PSM with the y axis representing the number of neutral losses observed for that PSM. There were no identified neutral losses in either ADMA IAP or SDMA IAP in the shControl cells. (right) The percentage of ADMA and SDMA neutral losses observed for shControl and shPRMT1 cells.