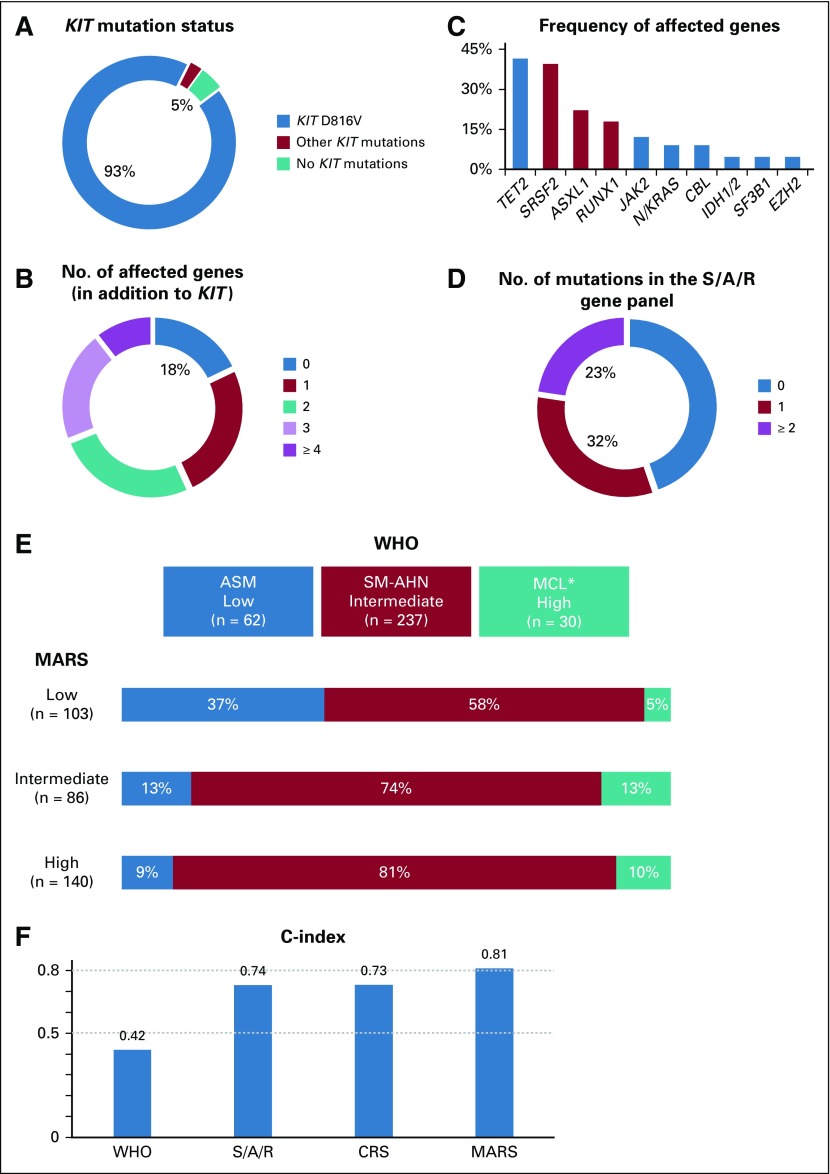
FIG 1.
(A) Relative frequency distribution of KIT mutations, (B) number of affected genes in addition to KIT, (C) frequency of mutations in addition to KIT, and (D) number of gene mutations in the SRSF2, ASXL1, and RUNX1 (S/A/R) panel of the training set. (E) Categorization of patients according to the mutation-adjusted risk score (MARS) of advanced systemic mastocytosis versus the WHO classification. Colored bars represent the WHO risk stratification (x-axis) in the context of the stratification on the basis of MARS (represented by the rows). (F) To evaluate the ability of the prognostic scores to predict outcome (with 0.5 indicating no discrimination and 1.0 indicating perfect prediction), the C-index is provided for WHO-based stratification, S/A/R mutation–based stratification, clinical risk score (CRS), and MARS. (*) The mast cell leukemia (MCL) cohort included patients with MCL with or without an associated hematologic neoplasm (AHN). ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis; SM, systemic mastocytosis.