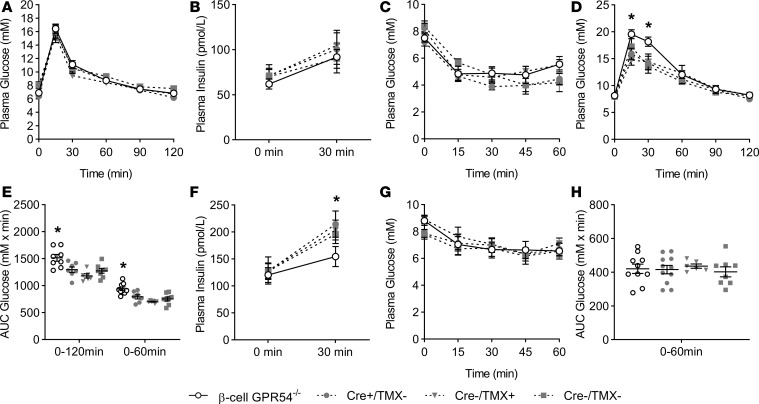
Figure 4. Glucose tolerance in female β cell GPR54–/– mice.
(A) There was no significant difference in glucose tolerance between nonpregnant adult female β cell GPR54–/– mice and any of the female control groups (Cre+/TMX–, Cre–/TMX+, and Cre–/TMX–). Similarly, the β cell GPR54–/– mice did not have (B) significantly altered plasma insulin levels, either fasted or after glucose, or (C) any change in insulin resistance when compared to any control group. (D) At day 16 of pregnancy β cell GPR54–/– mice had significantly impaired glucose tolerance at 15 and 30 minutes after glucose administration (2-way repeated-measures ANOVA; 15 minutes P = 0.028; 30 minutes P = 0.014) and (E) glucose AUC over the course of the test when compared with all control groups (1-way ANOVA; 0–120 minutes AUC P = 0.02; 0–60 minutes AUC P = < 0.001). (F) Pregnant β cell GPR54–/– mice did not have significantly altered basal fasting plasma insulin levels at day 16 of pregnancy; however, GPR54 knockdown did result in significantly reduced insulin release in response to i.p. glucose administration (2 g/kg) after 30 minutes when compared with all controls (1-way ANOVA, P = 0.045). (G) Pregnant β cell GPR54–/– mice did not have significantly different insulin sensitivity either at any individual time point or in (H) glucose AUC. Mean ± SEM; n = 7–9 (A–C); n = 7–12 (D–H); *P < 0.05.