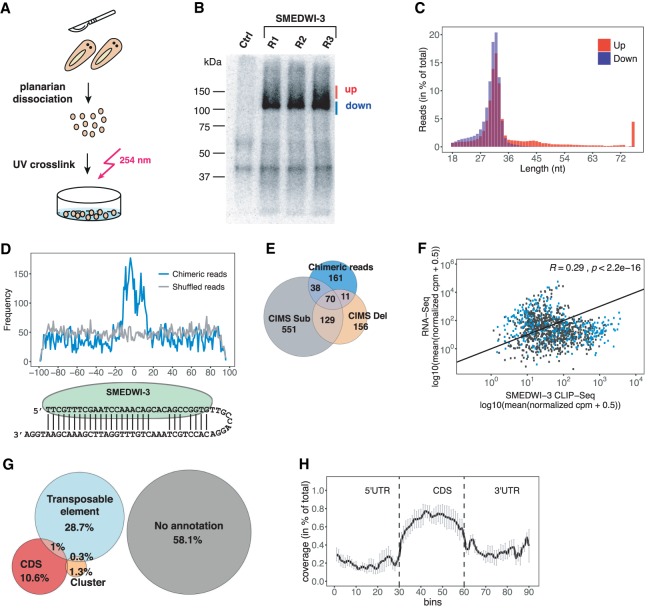
Figure 3.
Identification of SMEDWI-3-targeted transcripts by HITS-CLIP. (A) Schematic representation of HITS-CLIP in planarians. (B) Immunoprecipitated crosslinked SMEDWI-3–RNA complexes were radioactively labeled, separated on an 8% Bis-Tris gel, and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. CLIP libraries were prepared from RNA extracted separately from the upper and lower bands. Pre-immune serum served as negative control. (C) Length distribution of CLIP reads from the upper and lower bands. (D) Alignment of the piRNAs parts of chimeric reads onto the ±100-nt extended midpoint of mRNA fragments. An alignment of piRNAs to random mRNA fragments was used as a negative control. (E) Venn diagram representing the identified SMEDWI-3 CLIP targets carrying deletions, substitutions, and chimeric reads. (F) Scatter plot comparing log2 normalized CPM (counts per million) of mapped reads for CLIP-seq and RNA-seq data. Transcripts carrying chimeric reads are highlighted in blue. The Spearman's correlation coefficient is indicated. (G) The annotation of CLIP fragments to the planarian genome confirms the involvement of SMEDWI-3 in the posttranscriptional regulation of transposable elements and coding transcripts. (H) Density of the CLIP fragments mapping to 5′-UTRs, coding regions, and 3′-UTRs of coding genes. Each feature was divided into 30 bins. The mean density of CLIP fragments was calculated over the corresponding features. Error bars represent SE.