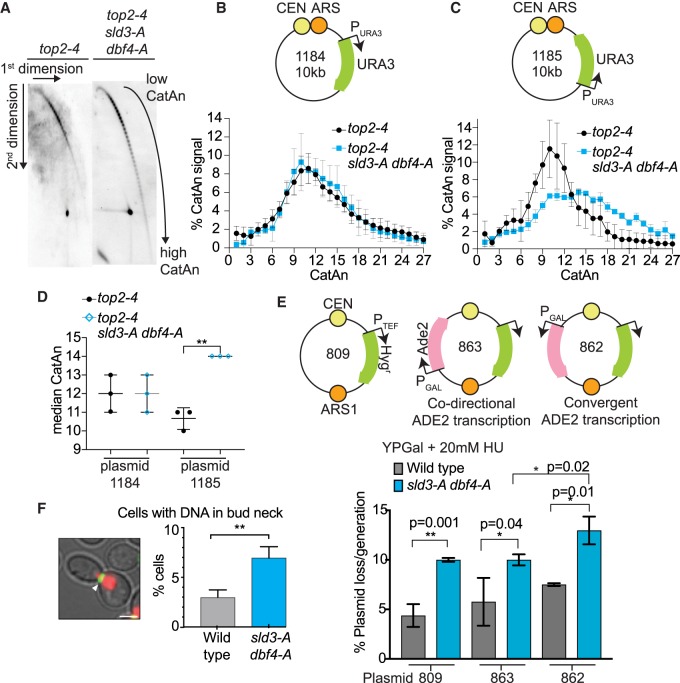
Figure 5.
Checkpoint inhibition of origin firing prevents excess catenation and chromosome loss. (A) Southern blots of 2D gels from yeast containing the plasmid 1185 (see C). The indicated yeast strains were arrested in alpha factor at 25°C, then switched to the nonpermissive temperature (37°C) for top2-4 and released into 0.033% MMS for 90 min. After nicking of DNA to remove supercoiling, the catenated forms (CatA) of the replicated plasmid can be discriminated. (B,C, top) Schematic diagram of plasmids with codirectional (1184) or convergent (1185) URA3 transcription relative to the direction of replication. (Bottom) Plot of the distribution of catenated isoforms of the plasmids 1184 (B) and 1185 (C) from the indicated strains. Error bars are SD, n = 3. (D) Graph of the median CatAn from B and C. Error bars are SD, n = 3. (E) Plasmid loss assay of the plasmids shown schematically above. Strains were grown overnight in YP galactose + 20 mM HU. Error bars are SD from n = 3. P-values are from paired t-tests. (F) Quantification of DNA in the bud neck after cytokinetic ring contraction. Error bars are SD from n = 3. Image of yeast (left) containing Htb2-mcherry (red) and myo1-GFP (green). Scale bar, 3 µm. A contracted myosin ring was considered to be <2 µm (white arrow).