Figure 1.
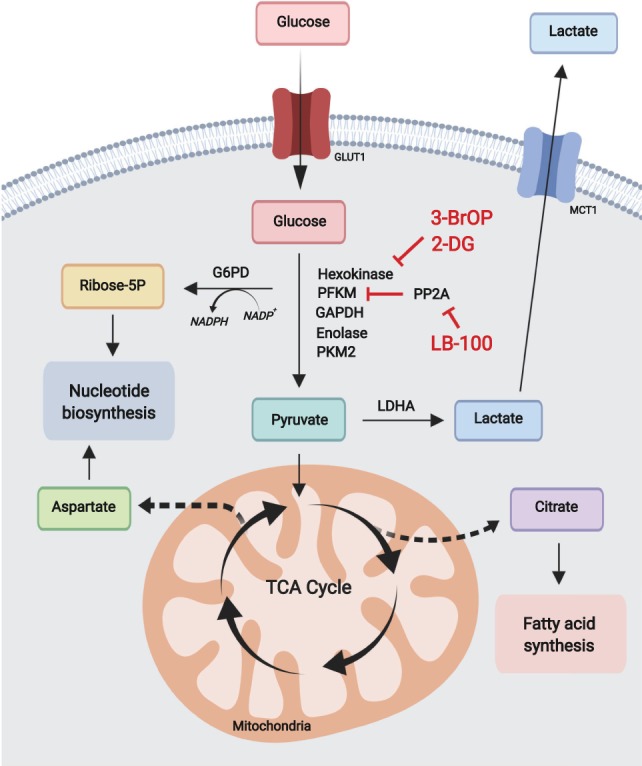
Glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway. Catabolically, glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate ultimately producing lactate, or acetyl-CoA in the TCA cycle for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Anabolically, glycolysis generates metabolic precursors for serine biosynthesis and supports redox potential and nucleotide biosynthesis via the pentose phosphate pathway. Most leukemias are highly dependent on glycolysis and can be targeted using glycolytic inhibitors.
