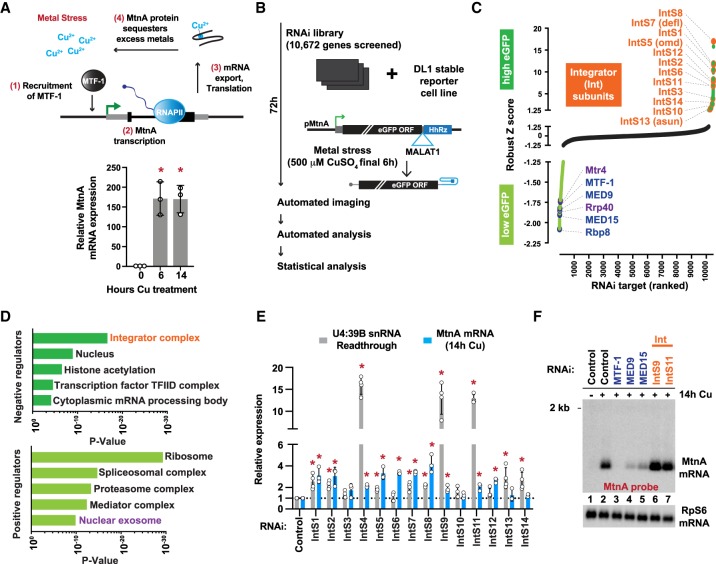
Figure 1.
The Integrator complex inhibits expression from the MtnA promoter during copper stress. (A, top) Upon metal stress, the transcription factor MTF-1 binds and induces transcription from the MtnA promoter, resulting in production of a protein that sequesters the excess metals to alleviate the stress. (Bottom) Drosophila DL1 cells were treated with 500 µM copper sulfate (CuSO4) for the indicated times, and RT-qPCR was used to measure endogenous MtnA mRNA expression. Data from three independent experiments were normalized to RpL32 mRNA expression and are shown as mean ± SD, (*) P < 0.05. (B) RNAi screen pipeline using DL1 cells stably maintaining an eGFP reporter driven by the MtnA promoter. The self-cleaving hammerhead ribozyme (HhRz) (Dower et al. 2004) generates the eGFP mRNA 3′ end, which is then stabilized by the MALAT1 triple helix structure (Wilusz et al. 2012). (C) Robust Z-scores of eGFP integrated intensity are shown. RNAi treatments that resulted in increased (Z-score >1.3, dark green) or decreased (Z-score < −1.3, light green) eGFP expression are marked, including Integrator subunits (orange), transcription regulators (blue), and RNA exosome components (purple). (D) Gene ontology (GO) analysis was performed to identify categories of genes that are enriched among the negative (Z-score >1.3) and positive (Z-score < −1.3) regulators of the eGFP reporter. (E) DL1 cells were treated with dsRNAs for 3 d to induce RNAi and depletion of the indicated factors. Expression of endogenous MtnA mRNA (after 14 h CuSO4 treatment) was quantified by RT-qPCR, and readthrough transcription downstream from the U4:39B snRNA was quantified by northern blotting. Data are shown as mean ± SD, N ≥ 3. (*) P < 0.05. (F) Representative northern blot of endogenous MtnA mRNA isolated from DL1 cells treated with dsRNA to induce RNAi of the indicated factor.