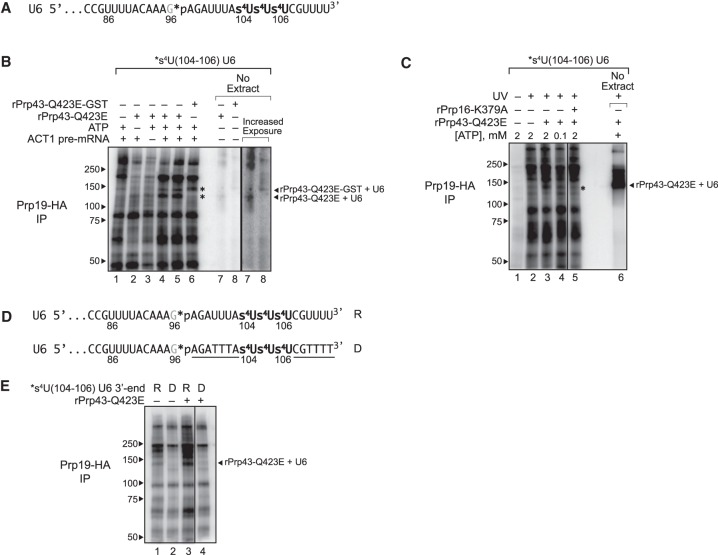
Figure 6.
The 3′ end of U6 snRNA interacts directly with Prp43p at the disassembly stage of splicing. (A) The 3′ end sequence of *s4U(104–106) U6, used for cross-linking, is shown with the location of 4-thio-U modifications (s4U) and the single 32P label (*p). (B,C) U6 cross-links to Prp43p in a splicing-dependent manner. Splicing of Cy5-ACT1 pre-mRNA was performed under the indicated conditions in extracts (ySCC1) reconstituted with *s4U(104–106) U6 and supplemented where indicated with either rPrp43p-Q423E, GST-tagged rPrp43p-Q423E, or rPrp16p-K379A; splicing reactions were monitored by PAGE (Supplemental Fig. S6B); control reactions were performed in the absence of extract as indicated. After cross-linking, spliceosomes were immunoprecipitated (IP) under native conditions by HA-tagged Prp19p, and then cross-links between U6 and spliceosomal proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE; control reactions were analyzed directly. Migration of protein size markers are indicated to the left, and the positions of U6 cross-linked to rPrp43p-Q423E or rPrp43p-Q423E-GST in the absence of extract are indicated to the right. An asterisk indicates migration of rPrp43p-Q423E or rPrp43p-Q423E-GST cross-linked to U6 in the absence of extract. See also Supplemental Figures S6, S7. (D) The 3′ end sequence of *s4U(104–106) U6, used for cross-linking, is shown with the location of 4-thio-U modifications (s4U), the single 32P label (*p), and DNA substitutions (underlined), where “R” indicates the U6 construct with RNA only at the 3′ end, and “D” indicates the U6 construct with the indicated DNA substitutions at the 3′ end. See also Supplemental Figure S7. (E) U6 cross-links to Prp43p in an RNA-dependent manner. Splicing, cross-linking, and immunoprecipitation were executed and analyzed as in B and C except that the U6 variants shown in D were utilized. The vertical lines in panels C and E represent lanes that were omitted for clarity.