Fig. 4. Application in encryption.
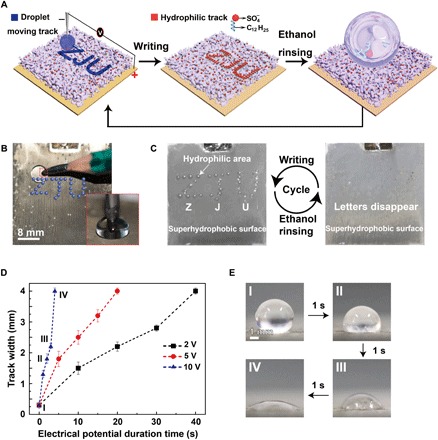
(A) Schematic of the information encryption process. A water droplet is dragged by a pencil connected to the negative pole of a power supply to write letters ZJU on the superhydrophobic surface connected to the positive pole of the power supply. The track turns hydrophilic. When the porous membrane is immersed in water or exposed to water steam, the ZJU letters will appear. Ethanol rinsing can turn the hydrophilic track superhydrophobic, allowing for repeatable usage. (B) The setup for the encryption application. Inset: A pencil behaving as a cathode immersed in a droplet sitting on the superhydrophobic surface. (C) Repeatable usage of the silver porous membrane in encryption applications. (D) The track width as a function of the duration time at 2, 5, and 10 V. The error bars are obtained on the basis of five independent measurements. (E) Photographs of the track created at 10 V for different times (photo credit: Yue Liu, Zhejiang University).
