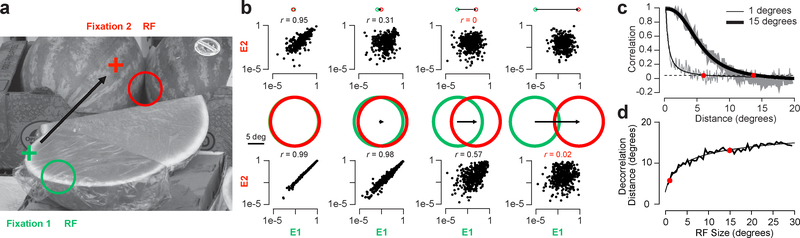
Figure 3.
Measuring decorrelation distance in natural images. a, Example image from a total of n = 392 images with a pair of RFs (RF) from the beginning (green circle) and end (red circle) of a saccade (black arrow). b, Scatter plots of the complex cell “energy” responses (E) for all pairs of RFs that have the same distance between them (n = 400 response pairs). The top row is data for RFs that are 1° in diameter and the bottom row is data for RFs that are 15° in diameter. The green and red circles indicate the RF size and the black arrow indicates the distance between RFs. Correlation values that fell below the decorrelation threshold are noted in red. c, Correlation measurements for all distances between RFs for the same two sizes (data from b are represented as single points in c). Gray lines are individual correlation measurements for each distance and the black lines are fits based on equation 16 in Online Methods. d, Decorrelation distances for all RF sizes (where data from c cross below the dashed line). The measured distances are plotted along with a fit based on equation 17 in Online Methods.