Figure 1.
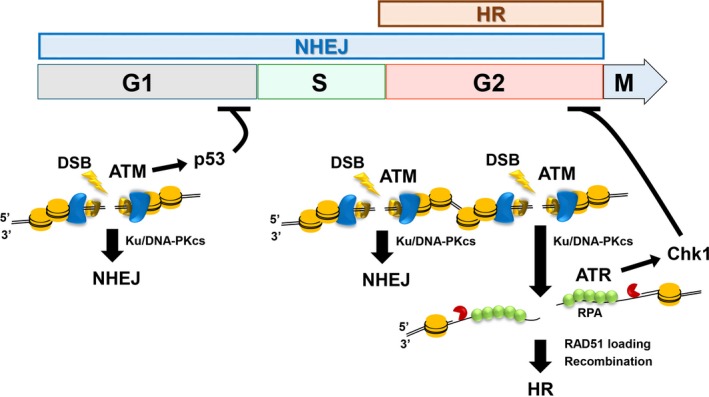
Orchestration of double‐strand break (DSB) repair and its associated signaling activity. DSBs are repaired by non‐homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homologous recombination (HR). NHEJ repairs DSBs throughout the cell cycle except for M phase in mammalian cells, whereas HR functions only in S/G2 phase following DNA replication. DSB ends undergoing NHEJ, which are not resected, activate ataxia‐telangiectasia mutated (ATM). In contrast, DSB ends that undergo resection by DNA nucleases promote HR. The Ku70/80 (Ku) and DNA‐dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA‐PKcs) complex binds to most DSB ends to protect them from DNA nucleases and thereby promote NHEJ. In G1 phase, an ATM/p53‐dependent pathway activates G1/S checkpoint arrest, whereas in G2 phase, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (ATR)/checkpoint kinase (Chk1) activates G2/M checkpoint arrest. As ATM is required for resection, ATM contributes to G2/M checkpoint arrest. RPA, replication protein A
