Figure 4.
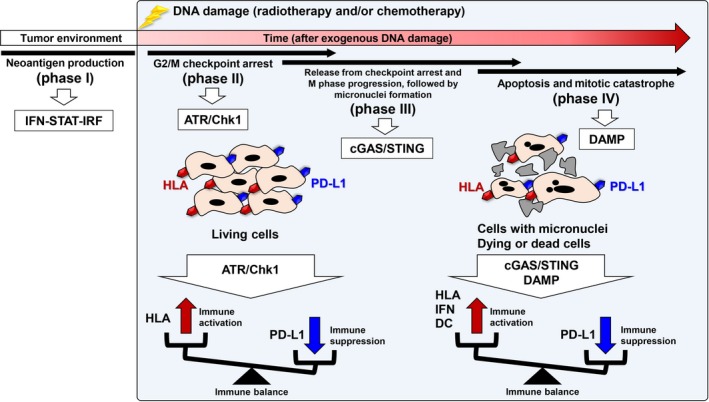
Chronology of the regulation of immune reactions induced by DNA damage‐dependent cellular responses. After DNA damage, cell cycle progression is arrested at the G2/M checkpoint. For example, 48‐72 h after exposure to 10‐Gy X‐rays, G2/M checkpoint arrest is released and G2 cells progress into M phase with double‐strand breaks, followed by the formation of micronuclei in the next G1. Finally, cancer cells receive a lethal dose of DNA damage. The upregulation of programmed death‐ligand 1 (PD‐L1) expression is induced in each process, although through distinct molecular mechanisms. Thus, anti‐PD‐1/PD‐L1 therapy could be given when the upregulation of PD‐L1 expression is induced under conditions of symmetrically stimulated immune activation. ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related; cGAS, cyclic GMP‐AMP synthase; Chk1, checkpoint kinase 1; DAMP, damage‐associated molecular pattern; DC, dendritic cell; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; IFN, interferon; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; STING, stimulator of interferon genes
