Figure 2.
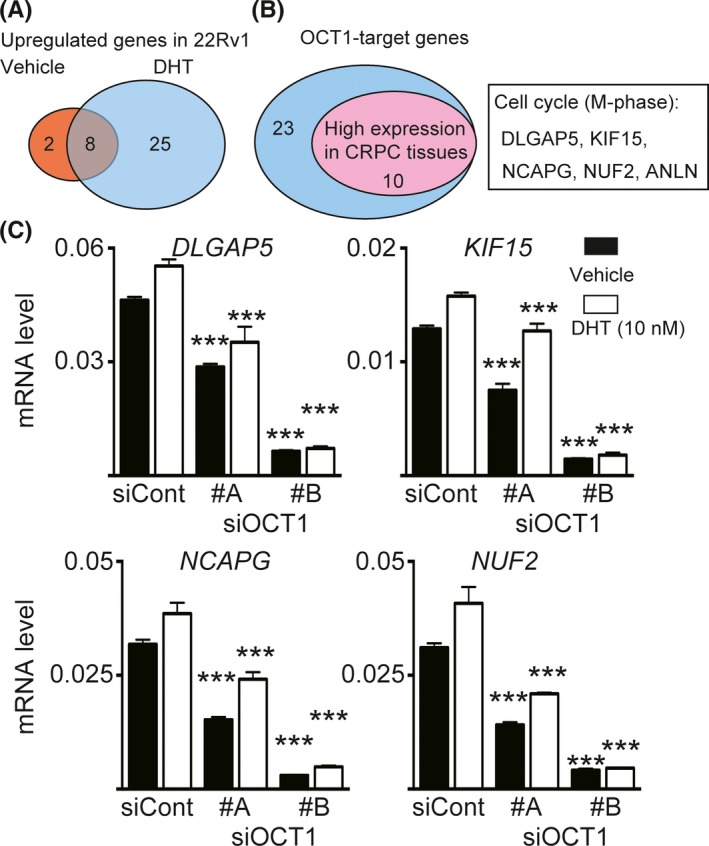
Identification of octamer transcription factor 1 (OCT1)‐target genes associated with castration‐resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). A, Candidate OCT1‐target genes in 22Rv1 cells. Among OCT1‐regulated genes in the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT),12 genes that satisfied the following three conditions were extracted: (i) upregulated in 22Rv1 cells compared with LNCaP cells in the absence of DHT; (ii) induced by DHT treatment in 22Rv1 cells; and (iii) high expression level was observed in 22Rv1 cells. Similarly, 10 genes were also extracted in the absence of DHT. B, Identification of OCT1‐target genes highly expressed in CRPC tissues. Using the Oncomine datasets (Varambally et al33 and Grasso et al32), we selected 10 candidate genes highly expressed in metastatic CRPC tissues. C, Validation of OCT1 regulation. 22Rv1 cells were treated with 10 nmol/L siControl or siOCT1 (#A and #B) for 48 h and then treated with 10 nmol/L DHT or vehicle for 24 h. We then measured mRNA expression levels of four candidate genes by qRT‐PCR. Results are presented as mean and SD (N = 3). ***P < 0.001, compared with siControl in the same condition. ANLN, anillin actin binding protein; DLGAP5, disks large‐associated protein 5; KIF15, kinesin family member 15; NCAPG, non‐SMC condensin I complex subunit G; NUF2, NDC80 kinetochore complex component
