Figure 4.
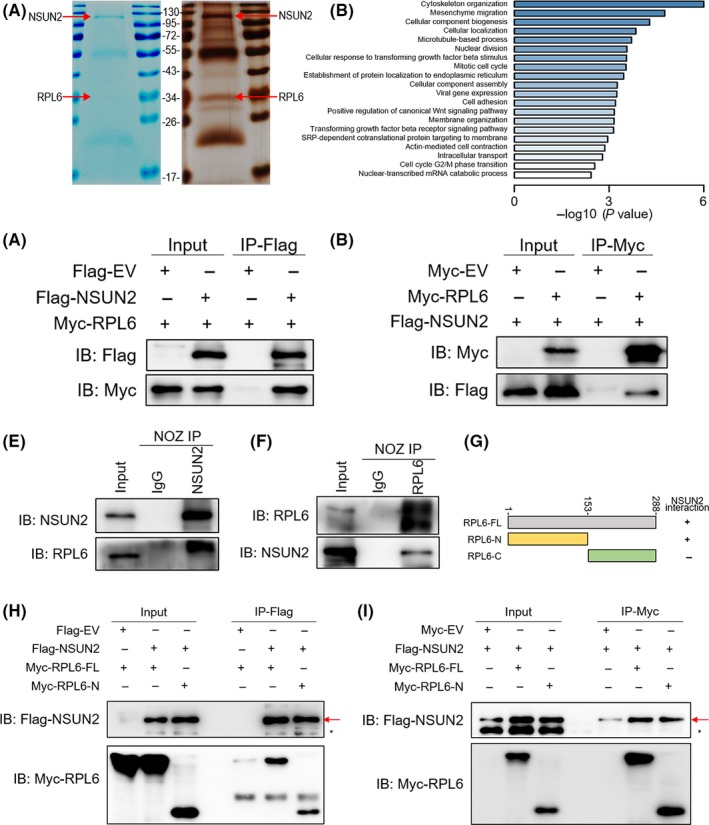
NSUN2 interacts with RPL6. A, Coomassie brilliant blue staining and silver staining of NSUN2 and its associated proteins. The red arrow represents SFB‐NSUN2 or endogenous RPL6. B, NSUN2‐associated proteins identified by IP‐MS were clustered by GO molecular function. C and D, Interaction between exogenous NSUN2 and RPL6. E and F, Interaction of endogenous NSUN2 and RPL6. NSUN2 and RPL6 showed a bona fide interaction between each other in NOZ cells. G, Schematic diagram of Myc‐RPL6 full‐length (RPL6‐FL), N‐terminal (RPL6‐N) and C‐terminal (RPL6‐C) constructs. The numbers represent amino acid residues. H and I, NOZ cells were co‐transfected with Flag‐NSUN2 and Myc‐RPL6 full‐length (Myc‐RPL6‐FL), N‐terminal (Myc‐RPL6‐N) or C‐terminal (Myc‐RPL6‐C) constructs as indicated. Interaction between NSUN2 and RPL6 depends on the N‐terminal of RPL6
