Figure 1.
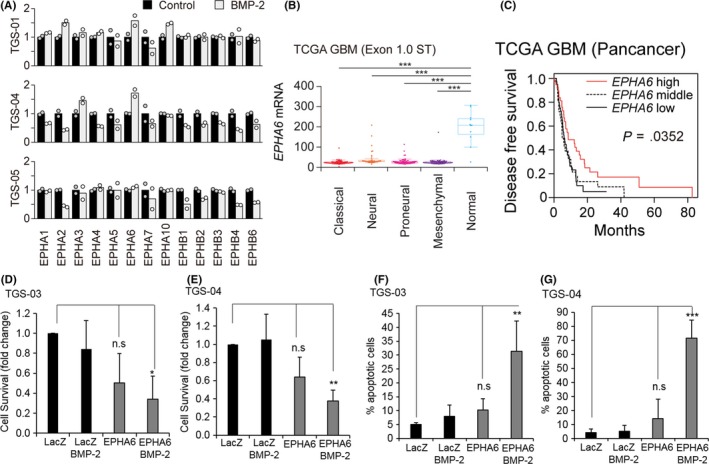
Erythropoietin‐producing hepatocellular carcinoma receptor A6 (EPHA6) is a glioblastoma tumor suppressor, which functions with bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP‐2) to induce apoptosis. A, EPHA and EPHB phosphorylation in patient‐derived glioma‐initiating cells (GIC) in response to BMP‐2 treatment evaluated by receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) phospho‐array analysis. TGS‐01, TGS‐04, and TGS‐05 were untreated (control, black bars) or treated with BMP‐2 (gray bars) for 24 h prior to analysis. Phosphorylation of the control conditions was normalized to 1 in each RTK. B, EPHA6 expression in normal brain or glioblastoma tissues in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets. ***P < .001. Glioblastoma was classified into four subtypes according to Verhaak et al.34 C, Kaplan‐Meier analysis of disease‐free survival of patients with glioblastoma from TCGA dataset (n = 112). Survival analysis was carried out using a log‐rank test. D, E, WST cell survival assay in TGS‐03 and TGS‐04 cells, respectively, after adenoviral transduction of LacZ control (ad‐LacZ) or wild‐type EPHA6 (ad‐EPHA6‐WT) in the presence or absence of BMP‐2 for 6 d. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01 and n.s. (not significant). F, G, Apoptosis assays by FACS analysis in TGS‐03 and TGS‐04, respectively. The same experimental setting as (D, E) was used, and cells were labeled with Annexin‐V and propidium iodide. Data represent mean ± SD of n = 4 (TGS‐03) and n = 3 (TGS‐04) independent experiments
