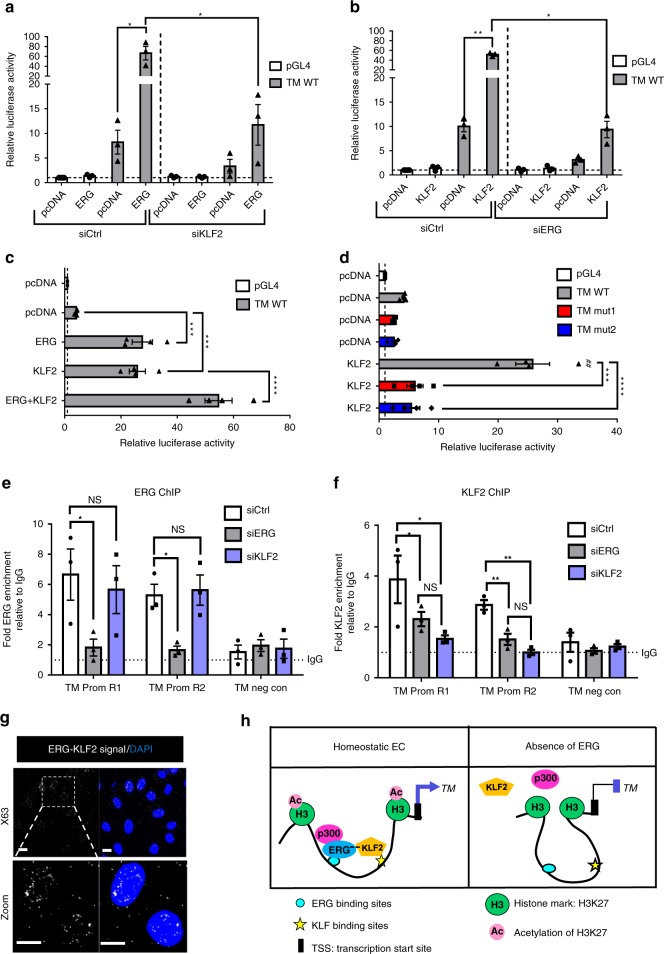
Fig. 6.
ERG cooperates with KLF2 to drive thrombomodulin expression. a–d TM promoter luciferase reporter assays. Values represent the fold change in relative luciferase activity over the empty pGL4 vector alone. b pcDNA or ERG expression plasmid (ERG) were co-transfected with a TM wild type (WT) promoter-luciferase construct (TM WT) in siCtrl or siKLF2-treated HUVEC, and luciferase activity was measured (n = 3 independent experiments). b pcDNA or KLF2 cDNA expression plasmid (KLF2) were co-transfected with TM WT promoter construct in siCtrl or siERG-treated HUVEC (n = 3 independent experiments). Graphical data presented in a and b are mean ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test. c pcDNA, KLF2 or both KLF2 and ERG plasmids were co-transfected with TM WT promoter construct (n = 4 independent experiments). Graphical data are mean ± s.e.m., ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, One-way ANOVA, compared to pcDNA-TM WT condition. d pcDNA or KLF2 plasmid were co-transfected with TM promoter constructs (TM WT, TM mutant 1 or TM mutant 2) (n = 4 independent experiments). Graphical data are mean ± s.e.m., ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, One-way ANOVA. ##P < 0.01, compared to pcDNA-TM WT, Student’s t-test. e, f ChIP-qPCR using primers to region R1 and R2 on e ERG- or f KLF2-bound chromatin from siCtrl, siERG or siKLF2-treated HUVEC (n = 3 independent experiments). Primers for a region within 5’UTR region of TM gene (TM neg con) were used as negative control. Data are shown as fold change over IgG. Graphical data are mean ± s.e.m., NS: Not Significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test. g Representative image of proximity ligation assay (PLA) for nuclear ERG-KLF2 interaction was performed on confluent HUVEC using anti-ERG and anti-KLF2 antibodies; nuclei are identified by DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. h Model: In homeostatic EC, ERG is required for p300 recruitment at the TM promoter region, leading to acetylation of H3K27 which opens the chromatin and allows KLF2 binding to the TM promoter. ERG binds to and cooperates with KLF2 to drive TM expression. In the absence of ERG, the chromatin is not accessible; KLF2 is not binding to the TM promoter and is not able to transactivate the TM promoter. Source data are provided as a Source Data file