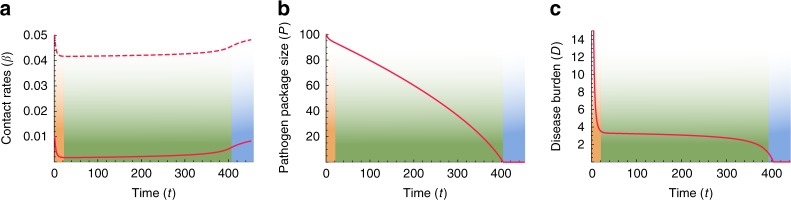
Fig. 3.
Disease-introgression dynamics between two species with symmetric initial conditions. The dynamics are described by the two-time-scales model (Fig. 2), following Eqs. (1)–(15). The initial conditions are assumed to be symmetric for the two species ( and ), and therefore, the dynamics for the two species are identical, indicated by red curves. a Between-species contact rates (, ) appear in solid curves, and within-species contact rates () appear in dashed curves (Eqs. (10)–(13)). b Pathogen package size (), measured as number or diversity of novel pathogens to which the species are vulnerable (Eqs. (14) and (15)). c Disease burden (), proportional to pathogen package size and to the impact of diseases on each of the species, (Eqs. (1) and (2)). Three phases are observed in the dynamics: (1) Initial response to heavy disease burden, with decreased contact rates (orange); (2) Long-lasting stable phase with low but steady levels of disease burden (green); (3) Destabilization following the release from disease burden and recovery to initial conditions (blue). The parameters for the scenario modeled are ; ; ; , with scaling parameters , , and