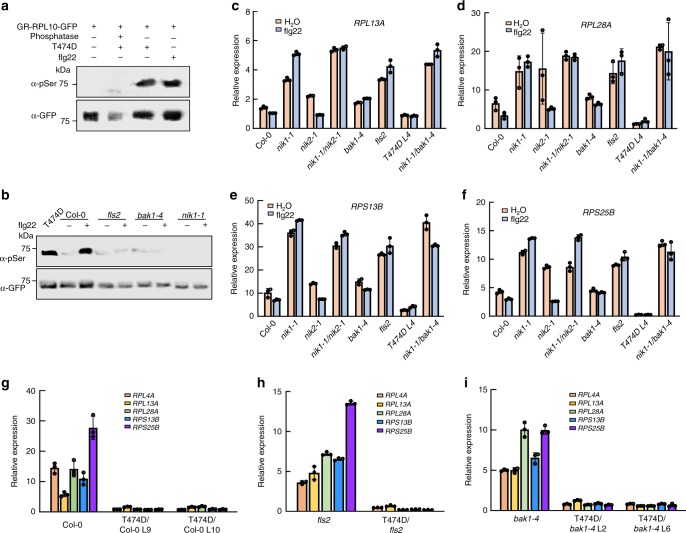
Fig. 6.
Flg22 induces RPL10 phosphorylation and the translation control branch of antiviral signalling in a NIK1-, FLS2/BAK1-dependent manner. a Flg22 treatment induces RPL10 phosphorylation. RPL10 phosphorylation was detected by immunoblotting with an α-phosphoserine (α-pSer) antibody (top) and RPL10 protein is shown using an α-GFP antibody. The experiment was repeated three times with identical results. b RPL10 phosphorylation requires the FLS2/BAK1 receptor complex. RPL10 was expressed in protoplasts isolated from Col-0, fls2, nik1-1 or bak1-4 mutants for 12 h, and then flg22 treatment was performed. T474D-mediated RPL10 phosphorylation was used as a positive control. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results. c–f Flg22-induced downregulation of RP13A, RPL28A, RPS13B and RPS25B is dependent on NIK1 and FLS2/BAK1. Seedlings of indicated plants were treated with flg22 for 3 h, and expression of ribosomal genes was analysed by qRT-PCR. Data are shown as the mean ± SE (n = 3). g Overexpression of NIK1-T474D in WT Col-0 suppresses expression of ribosomal genes. qRT-PCR analysis of RP expression levels in Col-0- and T474D-overexpressing lines. h, i FLS2 and BAK1 are not required for the suppression of ribosomal genes by NIK1-T474D overexpression. Ribosomal marker gene expression levels were detected in fls2, bak1-4 mutants and NIK1-T474D-overexpressing lines. The respective 95% confidence interval limits were estimated based on bootstrap resampling replicates of three independent (n = 3) experiments and three technical repeats. Source data are provided as a Source Data file