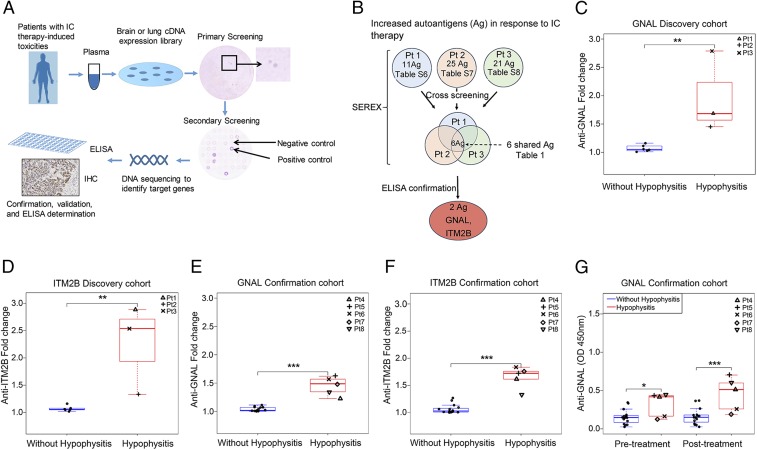
Fig. 1.
Plasma anti-GNAL and anti-ITM2B autoantibodies correlate with IC-therapy–induced hypophysitis. (A) Schematic illustration of the SEREX-based identification of IC-therapy–induced toxicity-related autoantibodies and confirmation process. (B) Workflow to identify autoantigens (Ag) by SEREX and to confirm hypophysitis-related autoantibodies. (C) Anti-GNAL and (D) anti-ITM2B autoantibody fold change in response to IC therapy in the plasma of discovery cohort patients (hypophysitis = 3; without hypophysitis = 6). (E) Anti-GNAL and (F) anti-ITM2B autoantibody fold change in the plasma of confirmation cohort patients (hypophysitis = 5; without hypophysitis = 15). (G) Anti-GNAL autoantibody levels in pre- and posttreatment in the confirmation cohorts. Values represent pre- and posttreatment levels, and fold changes represent increase from baseline in response to IC therapy. All boxplots have median center values. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.