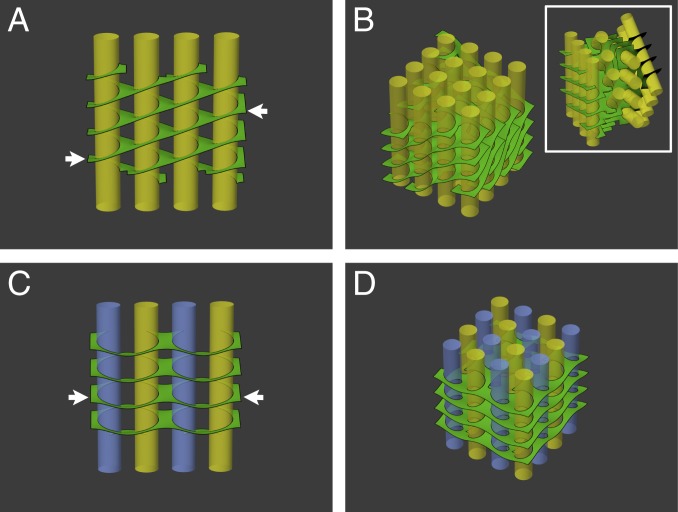
Fig. 5.
Surface energy minimization of networks assembled from various arrangements of helical elements. (A) Surface area minimization of a single file of grana (yellow) surrounded by right-handed helical structures, akin to the helical model (Fig. 1B), results in oppositely sloped long edges of the lamellar sheets (arrows). Extension of A to 2D arrays of grana columns requires either significant bending and twisting of the lamellae (B) or rigid, successive rotations of the grana files to match the orientation of their lamellar boundaries (B, Inset). (C) A single file of grana surrounded by alternating right- and left-handed helical membrane elements (indicated respectively by yellow and blue grana columns). The slope of the lamellar sheets at the boundary of the file is reduced to zero (compare arrows in A and C). (D) Extension of C to 2D arrays, with alternating handedness of the helical elements both between and within files, as observed experimentally, preserves the coorientation of the grana columns and allows the stroma lamellae to remain orthogonal to the grana cylinders.