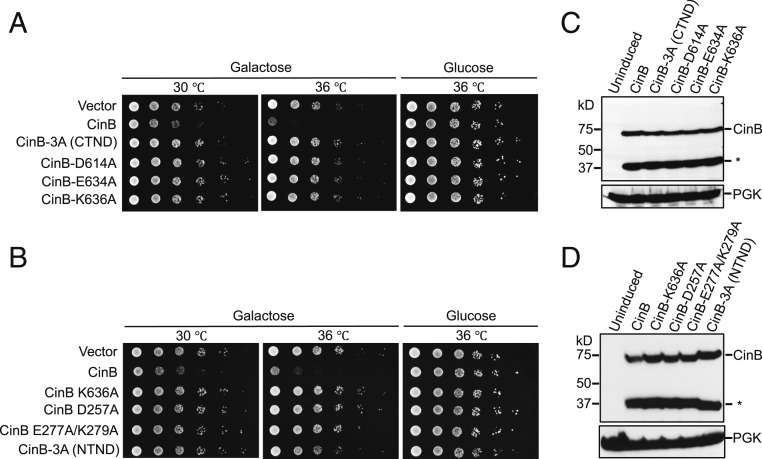
Fig. 4.
CinBwPip toxicity in the S. cerevisiae BY4741 strain. (A and B) All genes were N-terminally FLAG-tagged and cloned into pYES2, a galactose-inducible expression vector. Expression of wild-type CinB caused a temperature-dependent growth defect. Such growth defects were not observed in yeast expressing CinB with predicted inactivating point mutations in either the CTND (A) or NTND (B). All serial dilutions were done in triplicate with independent transformants. (C and D) Relative expression levels of WT and mutant CinB proteins. Equivalent numbers of yeast based on OD600 were lysed, and the lysates were resolved by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted for CinB by α-FLAG antibody; PGK served as a loading control. A fraction of CinB is proteolytically cleaved in yeast and the N-terminal fragment is labeled with an asterisk (SI Appendix, Fig. S3).