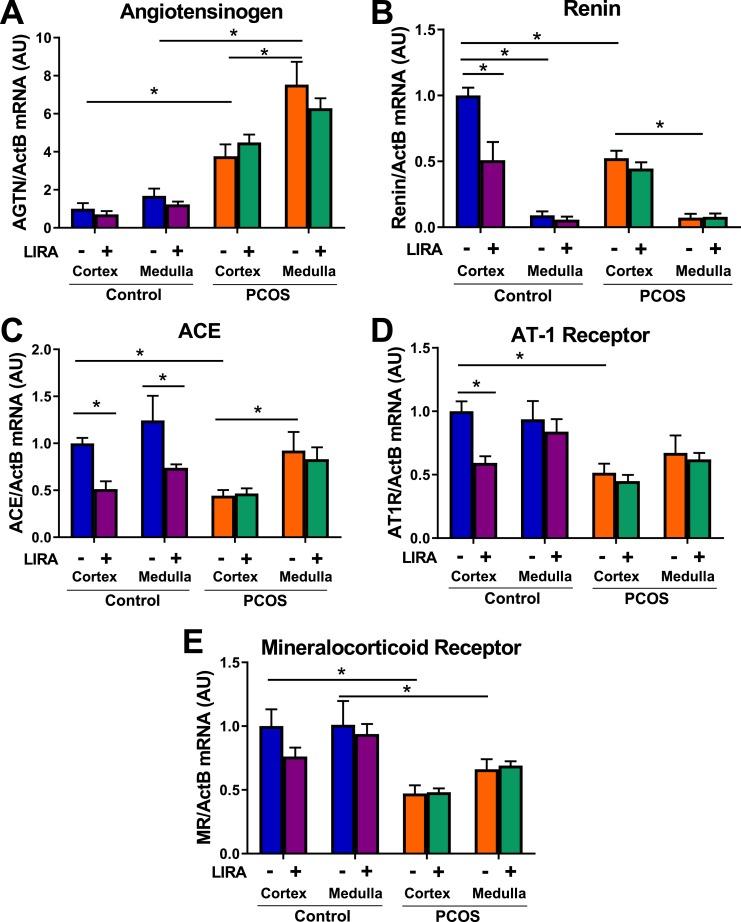
Figure 4.
Expression of intrarenal RAS components in postmenopausal PCOS rats. (A) Renal cortical and medullar mRNA expression of angiotensinogen were four and six times higher, respectively, in PCOS compared with control rats. Lira did not affect renal angiotensinogen mRNA expression. (B) Renal expression of renin was higher in the cortex compared with medulla in both groups. Renal cortical expression of renin was significantly higher in controls than in PCOS rats. Lira lowered renal cortical mRNA expression of renin in control rats but not in PCOS rats. (C) Renal cortical ACE mRNA expression was significantly decreased in PCOS rats; in contrast, no differences were observed in the renal medulla. Lira lowered renal ACE mRNA expression in the cortex and medulla of control rats and had no effect in PCOS. (D) Renal cortical expression of AT1R was significantly higher in controls than in PCOS rats. Lira lowered renal cortical mRNA expression of renin in control rats but not in PCOS rats. (E) Renal cortical and medullar mRNA expressions of mineralocorticoid receptor were higher in control rats. Lira did not affect renal mineralocorticoid mRNA expression. *P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by three-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc tests. Significant interaction was observed by three-way ANOVA only for renin, whereas it was not significant for all other analyzed genes. *P < 0.05. n = 5 to 7 per group.