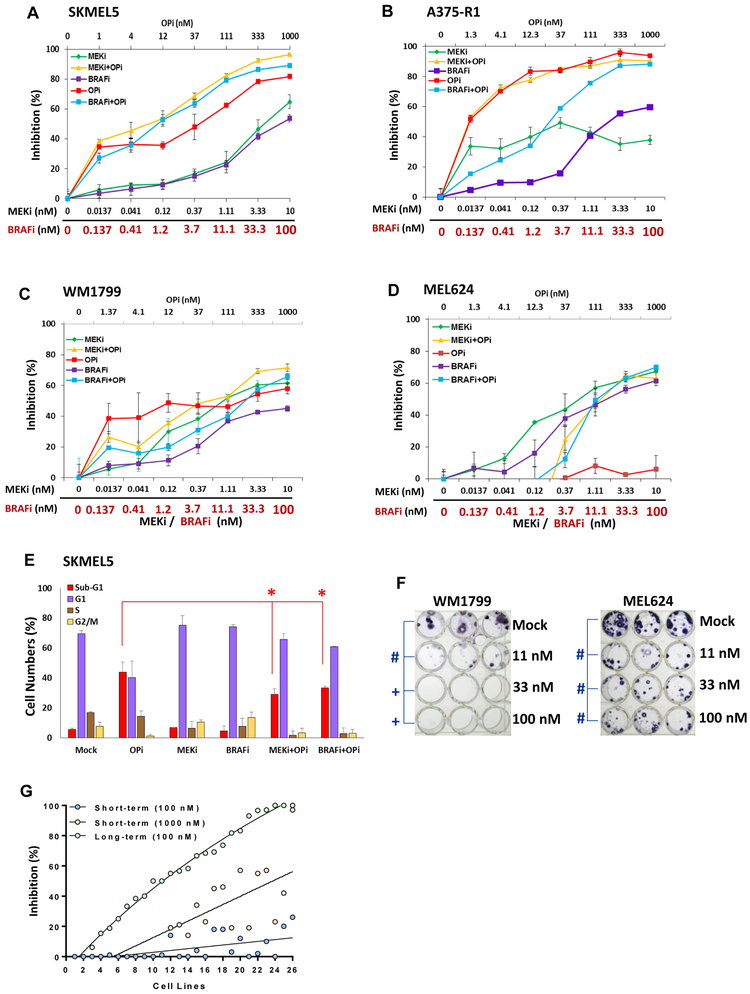
Figure 2. Effects of combining OPi with MAPK inhibitors (MAPKi) in vitro.
Inhibition of cell proliferation was determined after 72 h treatment with indicated concentrations of BRAFi, MEKi, OPi, and their combinations (OPi + BRAFi; OPi + MEKi) versus mock (dmso). Testing was performed on the MAPKi-resistant, BRAF-mutant (A) SKMEL5, (B) A375-R1, (C) WM1799, and (D) MEL624 melanoma cell lines. Bars represent average of triplicates; error bars, SD. (E) Propidium Iodide-cell cycle analysis of the SKMEL5 cell line following 72 h treatment with BRAFi, MEKi, OPi, or their combinations. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle, as well as dead cells (sub-G1), are indicated. Bars represent average of triplicates; error bars, SD. Significant differences by T tests are indicated by asterisks (p<0.05). (F) WM1799 and MEL624 cells were treated with mock or OPi at the doses shown for 30 days; media/drug was changed every 72 h. Colonies were stained with crystal violet. Significant differences of p<0.01 are indicated by hash (#), and p<0.001 by plus (+) symbols. (G) The short-term (72 h) cell proliferation and the long-term (30 days) colony formation assays in OPi-treated cells were performed on melanoma patient-derived cell lines. Percentages of short-term proliferation inhibition by 100 nM and 1000 nM OPi concentrations, and long-term colony formation inhibition by 100 nM were plotted in a curve fit plot, supervised with cell lines in ascending order of sensitivity (% inhibition) in the colony formation assay; data was derived from triplicate treatments.