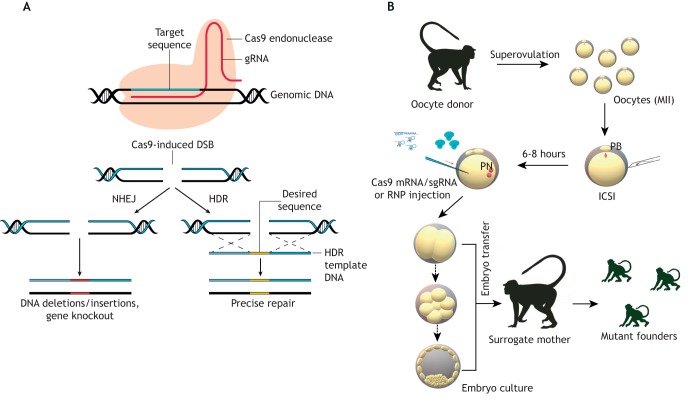
Fig. 2.
Schematic of the experimental approach to generate gene-edited monkeys via CRISPR/Cas9. (A) Schematic of the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The gRNA tethers the Cas9 endonuclease to a specific genetic locus in a sequence-specific manner. The Cas9-induced DSBs are then repaired by intrinsic DNA repair mechanisms. Generally, the simpler error-prone NHEJ results in an indel or frameshift mutation that inactivates the gene. If a repair template is provided, the more precise HDR system can result in a specific alteration, such as a disease-causing point mutation. (B) Genome editing in NHPs. The first step requires harvesting and fertilization of oocytes, which can then be edited via injection of CRISPR components (either Cas9 and sgRNA RNPs, or Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA molecules). The edited embryos are then cultured and implanted in a surrogate mother. dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; ICSI, intracytoplasmic sperm injection; MII, metaphase II stage; PB, polar body; PN, pronucleus; RNP, ribonucleoproteins.