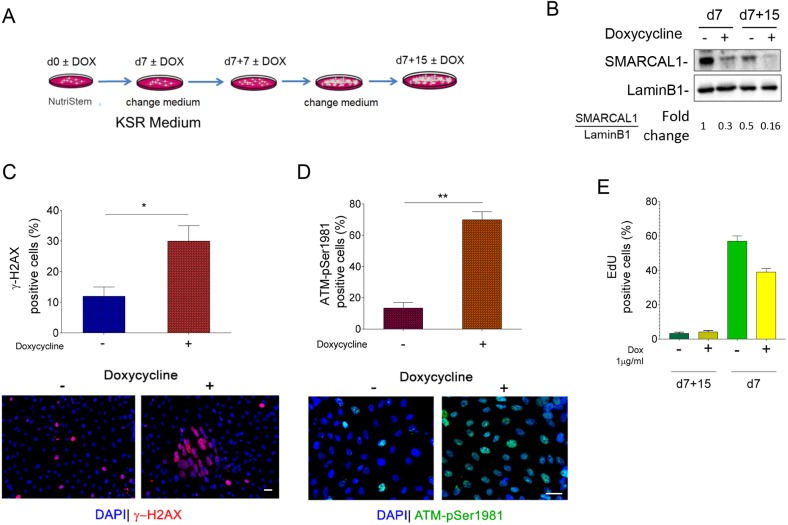
Fig. 6.
Increased levels of replication-dependent DNA damage and DDR activation persist in SMARCAL1-depleted iPSCs upon their differentiation. (A) Schematic of the early differentiation protocol of iSML1 iPSCs, treated with or without doxycycline (DOX) as indicated. (B) Western blot analysis of levels of SMARCAL1 depletion after 7 and 15 days from spontaneous multi-lineage differentiation. Lamin B1 was used as loading control. (C,D) Analysis of DNA damage accumulation or DDR activation in iSML1 iPSCs after spontaneous multi-lineage differentiation. The graphs (top) show the percentage of γ-H2AX-positive nuclei (C) or ATM-pSer1981-positive nuclei (D) for each endpoint. Representative images are shown (bottom). (E) Analysis of replicating cells in SMARCAL1-depleted iPSCs. EdU labelling (30 min) was used to mark replicating cells. The graph shows the percentage of EdU-positive cells after 15 days of early differentiation treated or not with DOX. As reference, the values of EdU-positive cells in respect to the corresponding undifferentiated iSML1 iPSCs are included (d7). Data are mean±s.e.m. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P≤0.01 (two-way ANOVA test). Scale bars: 10 µm.