Figure 2.
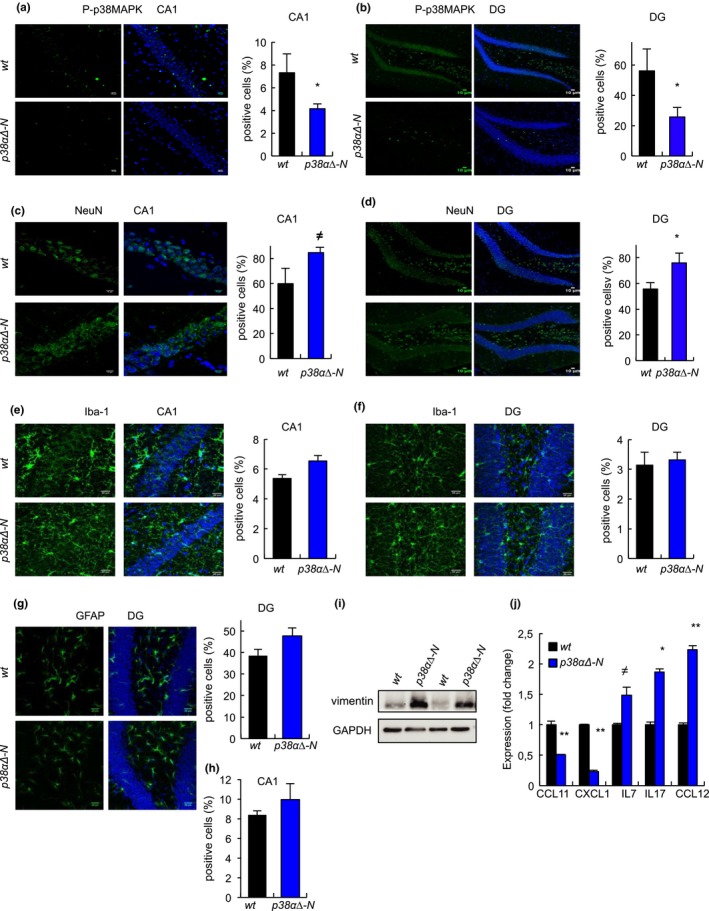
Genetic deletion of p38α in neurons prevents age‐associated neuronal loss (a, b) Representative immunofluorescence and quantification for phosphorylated p38MAPK (P‐p38MAPK) relative to DAPI in (a) CA1 and (b) DG of aged (over 24‐month‐old) wt and p38α∆‐N mice (n ≥ 4). (c, d) Immunofluorescence and quantification for NeuN+ cells in (c) CA1 and (d) DG of aged wt and p38α∆‐N mice (n ≥ 4). (e, f) Immunofluorescence and quantification for Iba‐1+ cells in (e) CA1 and (f) DG of aged wt and p38α∆‐N mice (n ≥ 4). (e, f). (g, h) Immunofluorescence and quantification for GFAP+ cells in (g) CA1 and (h) DG of aged wt and p38α∆‐N mice (n ≥ 4). (i). Immunoblot of vimentin from ex vivo hippocampal tissue from wt and p38α∆‐N aged mice (n = 2). (j) Quantification of differentially expressed cytokines in ex vivo hippocampal tissue from aged wt and p38α∆ mice (n = 2)
