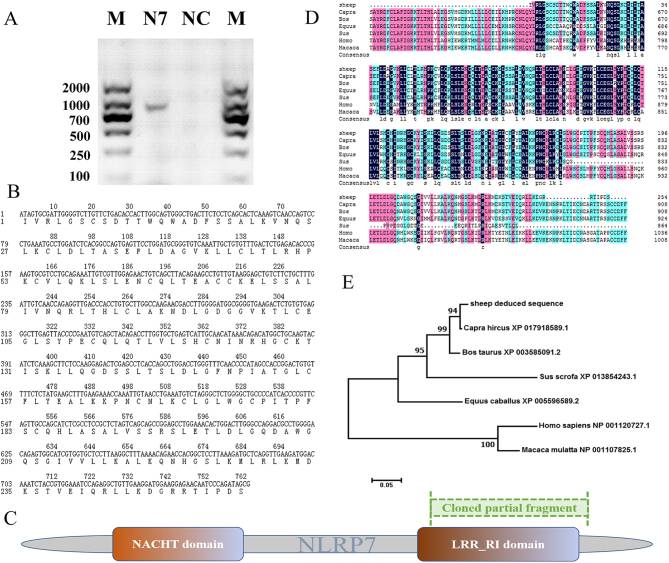
Figure 4.
Cloning and characterization of ovine NLRP7 partial CDS.(A) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) amplification of the ovine NLRP7 partial CDS. Lane N7, NLRP7 amplicon; NC, negative control; M, 2000 bp DNA marker. The amplified ovine CDS is 763 bp.(B) Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of cloned NLRP7 partial fragment of sheep. The deduced amino acid sequence (254 residues) is under the nucleotide sequence and numbered on the left. These sequence data have been submitted to the GenBank under an accession number MF197687.(C) Scheme of the cloned fragment (marked in green) compared to the full length of NLRP7 (marked in gray). NACHT and LRR_RI are two major domains of NLRP7. (D) Multiple alignments of NLRP7 amino acid sequence in different species including Capra hircus, Bos Taurus, Homo sapiens, Macaca mulatta, Sus scrofa, Equus caballus. The multiple alignments were produced using ClustalX, in which black color indicates positions that have a single, fully conserved residue (100% similarity) as opposed to pink (>75%), aqua (>50%), respectively. Dashes indicate gaps. (E) Phylogenetic tree of mammalian NLRP7 homologs was conducted in MEGA7 using the Neighbor-Joining method, with the sum of branch length = 0.86954469. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test are shown next to the branches.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a