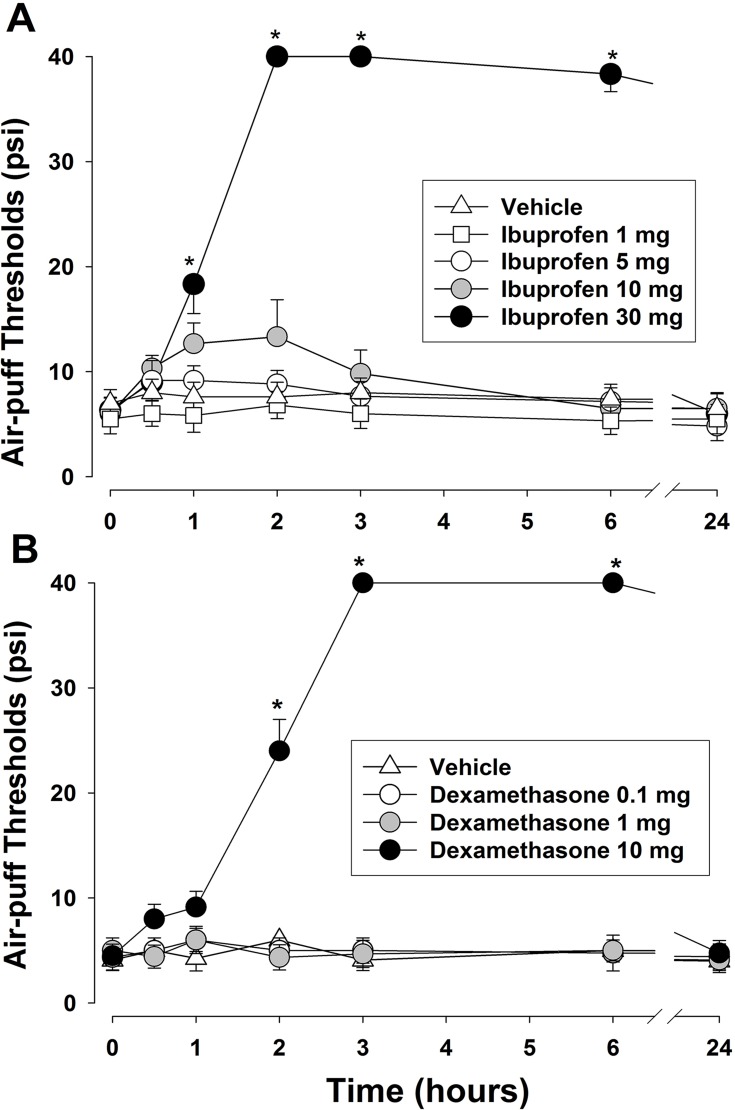
Figure 1.
Effects of the intraperitoneal administration of ibuprofen (A) or dexamethasone (B) on the air-puff thresholds in rats with an inferior alveolar nerve injury. A high dose of ibuprofen (30 mg/kg) or dexamethasone (10 mg/kg) produced significant antiallodynic effects compared with the vehicle-treated control group. These effects persisted for over 6 hrs after the injection and dissipated within 24 hrs. Neither the intraperitoneal injection of the vehicle nor low doses of ibuprofen (1, 5, 10 mg/kg) or dexamethasone (0.1, 1mg/kg) affected the air-puff thresholds. The values shown are the mean ± SEM. There were 6 animals in each group. *p < 0.05, vehicle- vs. drug-treated group.