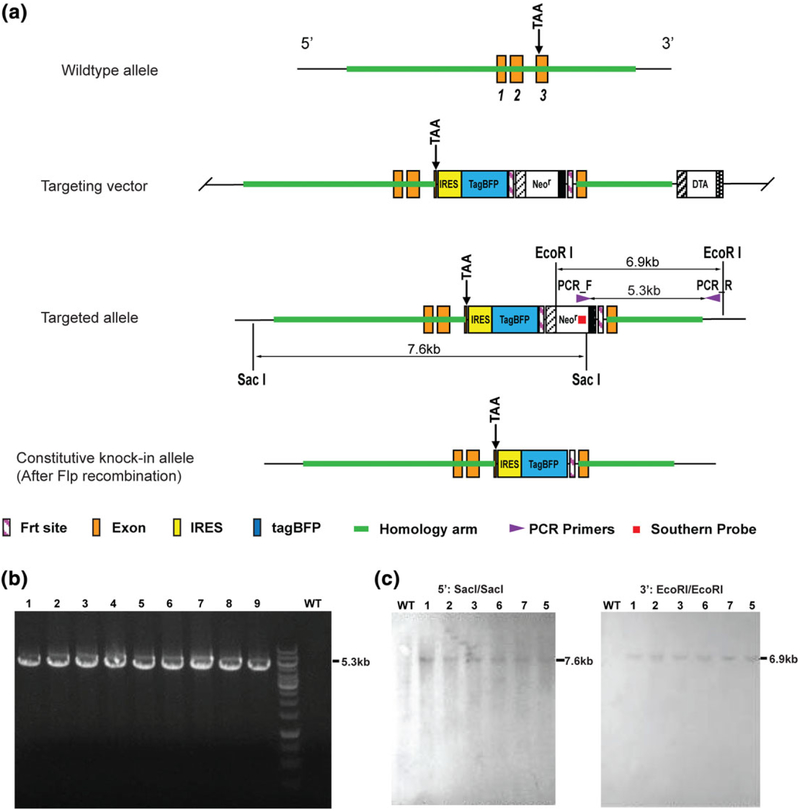
FIGURE 1.
Generation of Nppa-tagBFP reporter knock-in mouse line. (a) Schematic illustration of the gene targeting strategy. IRES-tagBFP-FRT-NeoR-FRT cassette was inserted into 3′-UTR of the Nppa gene locus. The NeoR gene cassette is flanked by two FRT sites. By homologous recombination, the mice carrying IRES-tagBFP-FRT-NeoR-FRT cassette (targeted allele) were generated. By cross breeding the chimera mice with FLP transgenic mice, Nppa-tagBFP knock-in mice carrying constitutive knock-in allele were generated by deleting NeoR cassette. (b) PCR screening for the targeted ESCs using the indicated PCR primers in (a). Nine expanded clones demonstrated expected size of PCR band (5.3 kb). A wild type (WT) clone did not show the band. (c) Southern blot analyses to confirm the correctly targeted ESC clones. Using six (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7) of nine PCR positive ESC clones, restrictive digestions with the indicated enzymes and hybridizations with the indicated southern probe in (a) were performed. Targeted ESCs for Nppa-tagBFP knock-in displayed 7.6 kb (with SacI) and 6.9 kb (with EcoRI) bands, whereas WT ESCs did not show any band. The southern blot results confirmed that all six expanded clones (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7) were correctly targeted