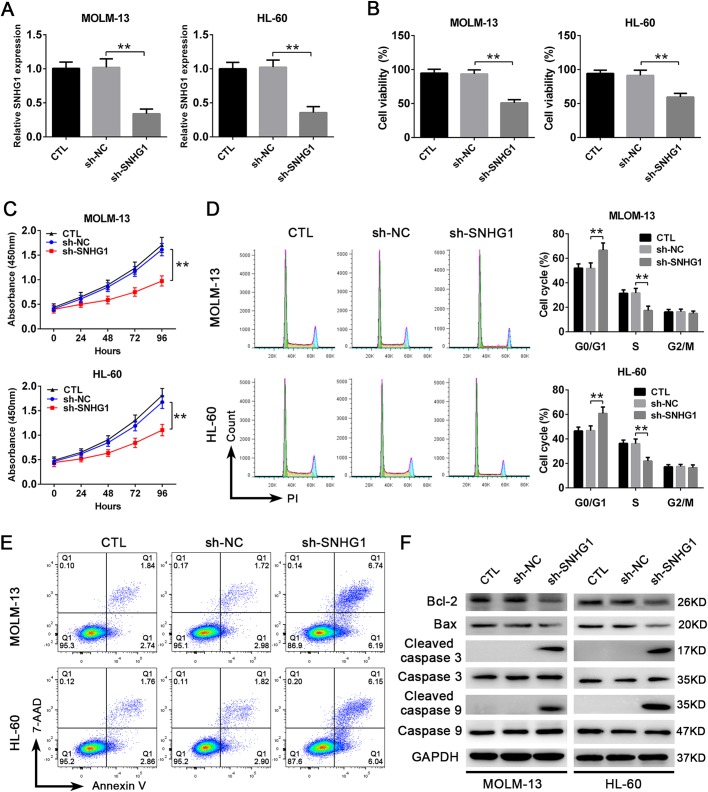
Fig. 2.
SNHG1 facilitates the proliferation and cell cycle progression and inhibits the apoptosis of AML cells. (A) The reduced expression of SNHG1 in MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells after being transduced with lentivirus expressing shRNA against SNHG1 (sh-SNHG1) or scrambled shRNA (sh-NC) (n=6). (B) The viability of MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells after knockdown of SNHG1, determined by Trypan Blue exclusion (n=6). (C) The proliferation of MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells after knockdown of SNHG1, detected by CCK-8 assay (n=6). (D) Cell cycle analysis of HL-60 and MOLM-13 cells after knockdown of SNHG1, measured by flow cytometry (n=6). (E) The apoptosis of MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells after knockdown of SNHG1, determined by flow cytometry (n=6). (F) Western blots detecting the expressions of anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic proteins in MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells after knockdown of SNHG1 (n=6). **P<0.01.