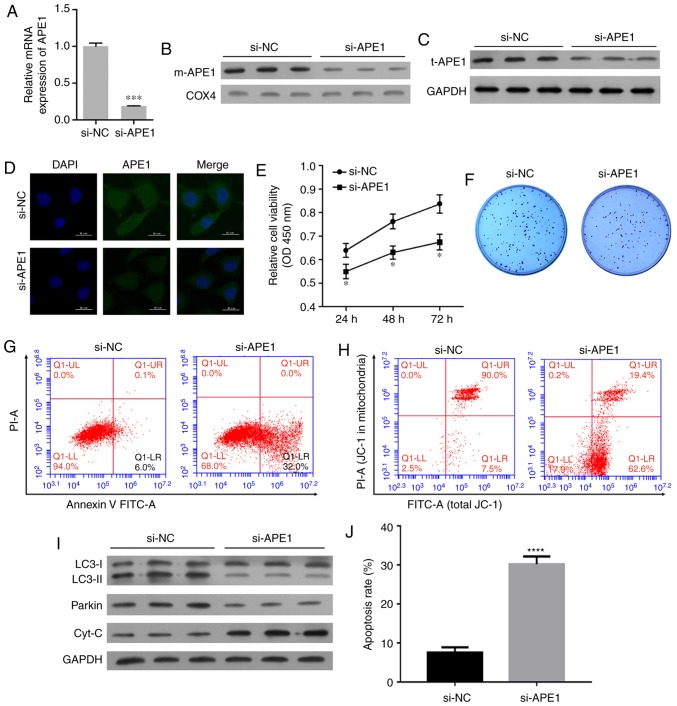
Figure 3.
APE1 knockdown increases the cisplatin sensitivity of A549/DDP cells. A549/DDP cells were transfected with small interfering RNA (si-APE1 or si-NC). (A) Transfection efficiency was assessed by qPCR. (B) The levels of mitochondrial APE1 (m-APE1) in the transfected A549/DDP cells were analyzed by western blotting. COX4 was used as loading control for mitochondrial APE1. (C) The total APE1 (t-APE1) protein levels in transfected A549/DDP cells were analyzed by western blotting. GAPDH was used as loading control. (D) Immunofluorescence assays were performed to assess the total APE1 levels in A549/DDP cells after transfection. (E) Transfected A549/DDP cells were treated with 15 µmol/l cisplatin for 24 h, and their viability was assessed by the CCK-8 assay. (F) Colony formation assays were performed to analyze the colony formation efficiency of the transfected A549/DDP cells. (G) The transfected A549/DDP cells were treated with cisplatin, and their rate of apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. (H) Flow cytometry was used to analyze the distribution of JC-1 after transfection. (I) The transfected A549/DDP cells were subjected to fractionation to obtain the cytosolic fraction. Western blot analysis was performed to analyze the levels of LC3, total cytochrome c, and Parkin. (J) The cell apoptosis rate is shown in a histogram. GAPDH was used as loading control. Data represent the results obtained from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM of triplicate samples). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001 vs. the si-NC group. APE1, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3.