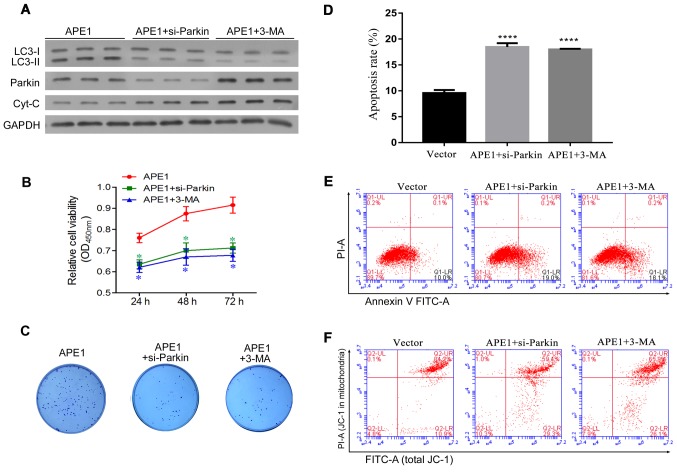
Figure 4.
Parkin-mediated mitophagy plays an important role in the APE1-induced cisplatin resistance of A549 cells. A549 cells were first transfected with an APE1 overexpression plasmid. Next, the APE1-overexpressing A549 cells were transfected with small interfering RNA (si-Parkin or si-NC) or treated with 3-MA. (A) A549 cells after the relevant transfections (APE1, si-Parkin or si-NC) and their indicated treatment were subjected to fractionation to obtain the cytosolic fraction. Western blot analysis was performed to analyze the levels of LC3, total cytochrome c, and Parkin in the cytosolic fraction. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Following the indicated transfection and treatment, the A549 cells were co-cultured with 3 µmol/l cisplatin for 24 h, and their viability was assessed by the CCK-8 assay. (C) Colony formation assays were performed to analyze the colony formation efficiency of the transfected A549 cells after they had received their indicated treatment. (D) The cell apoptosis rates are shown in a histogram. (E) The apoptosis rates of the transfected A549 cells treated or not with 3-MA were analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) The distribution of JC-1 in the transfected A549 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 and ****P<0.0001 vs. the APE1 group. 3-MA, 3-methyladenine (an autophagy inhibitor); APE1, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3.