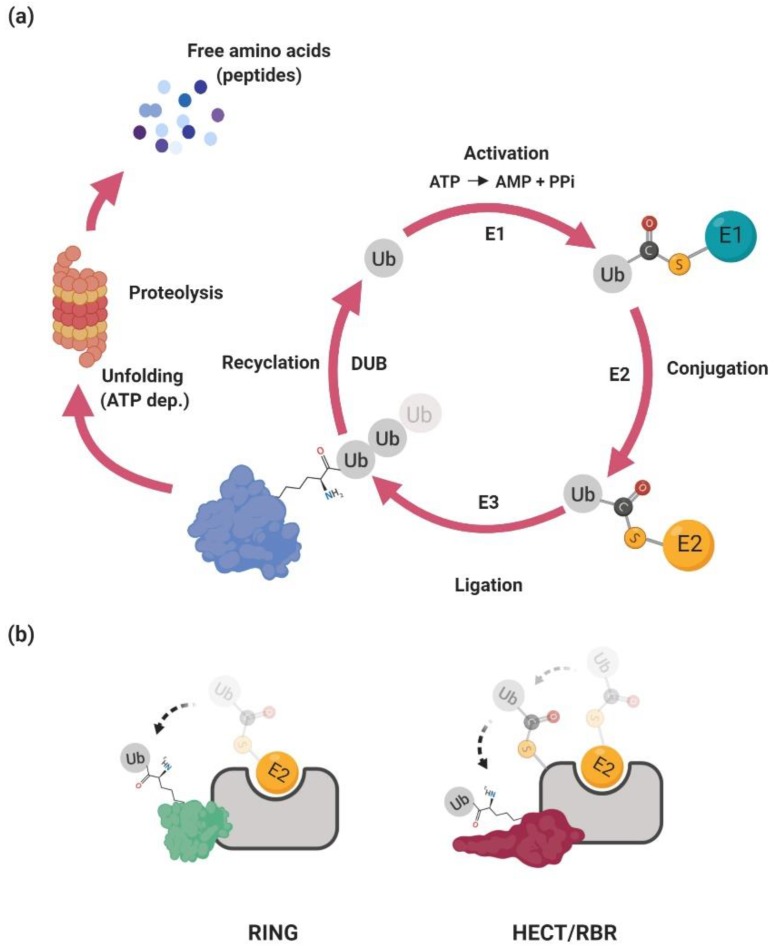
Figure 1.
The ubiquitin–proteasome system. (a) The mature free ubiquitin monomer protein is either recycled from the ubiquitinated substrate or cleaved from the polyubiquitin precursor. Both of these reactions are catalyzed by deubiquitinases (DUBs). Ubiquitin is then activated (E1), conjugated (E2), and finally ligated to the cognate substrate via ubiquitin ligases (E3). The polyubiquitinated substrate is later transferred to the proteasome, unfolded, and proteolytically degraded to small peptides or free amino acids. For more details see the text. (b) RING E3s catalyze the direct transfer of ubiquitin from E2∼ubiquitin to the substrate. HECT (homologous to E6AP C-terminus), and RBR (RING-between-RING) E3s accept ubiquitin from E2 to form an E3∼ubiquitin thioester intermediate via transthiolation reaction. For more details see the text.