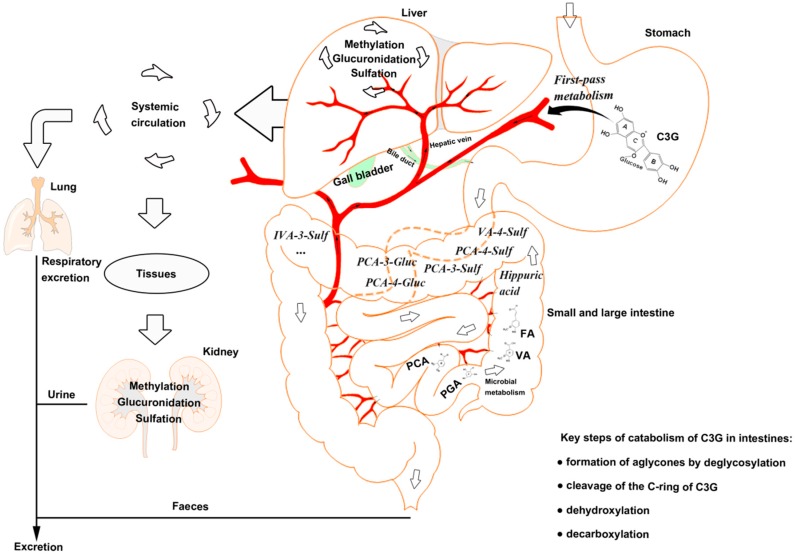
Figure 1.
The catabolism process of cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G) in an organism. C3G can be hydrolyzed to its aglycone by enzymes in the small intestine, and further degraded to phenolic compounds by gut microbiota. Microbial catabolism of C3G in the distal small intestine and large intestine is performed by the cleavage of the heterocyclic flavylium ring (C-ring), followed by dehydroxylation or decarboxylation to form multistage metabolites, which enter the liver and kidney by circulation. C3G, cyanidin-3-glucoside; FA, ferulic acid; PCA, protocatechuic acid; PGA, phloroglucinaldehyde; VA, vanillic acid.