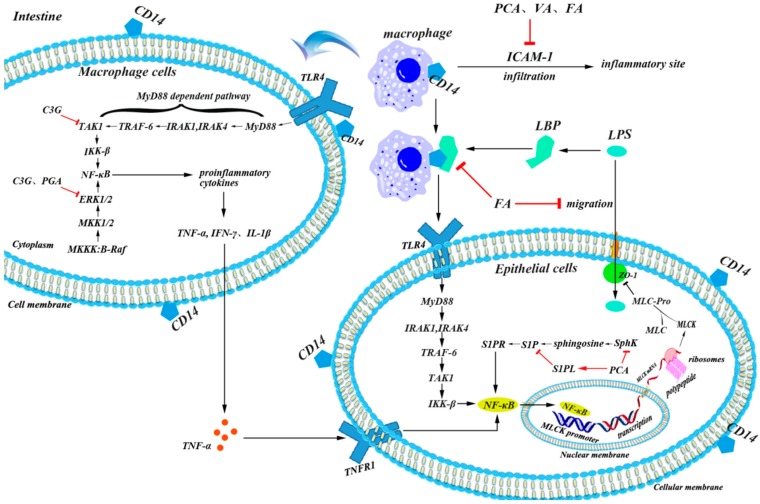
Figure 4.
Potential mechanisms of C3G&C3G-Ms in attenuating intestinal inflammation. C3G and its phenolic metabolites mainly modulate inflammation by three ways, first, to suppress the production of chemotactic factors such as ICAM-1 and thus alleviate inflammatory infiltration, second, to down-regulate inflammatory pathways such as TAK1-mediated MAPK pathway and SphK/S1P mediated NF-κB pathway, finally, the down-regulated inflammatory pathways, and up-regulated antioxidant pathway, as mentioned in Figure 3, will maintain sufficient expression of tight junction proteins such as ZO-1 to promote normal intestinal barrier function, and thus prevent LPS from entering mucosal cells. C3G, cyanidin 3-glucoside; FA, ferulic acid; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; PCA, protocatechuic acid; PGA, phloroglucinaldehyde; SphK, Sphingosine kinases; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; TAK1, transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase-1; VA, vanillic acid.