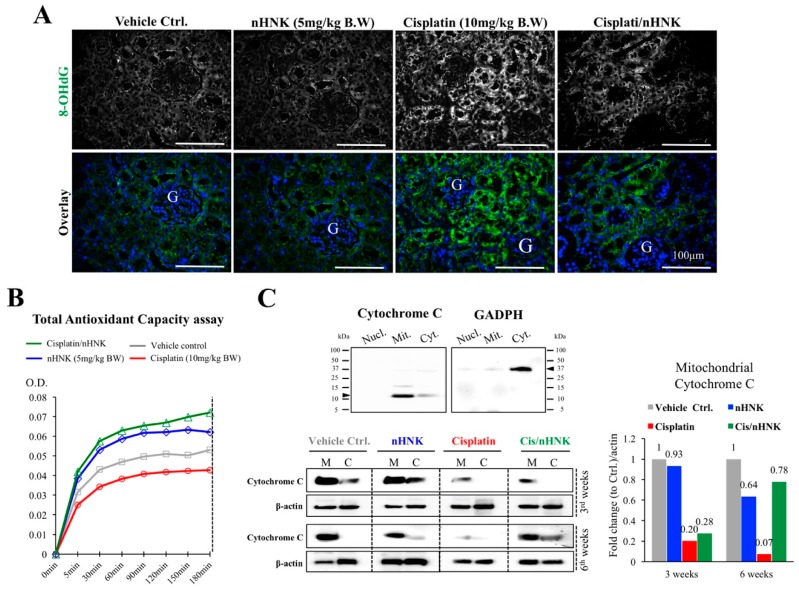
Figure 4.
Oxidative stress assessments on the reduction of oxidative damages and improved antioxidant capacity in nHNK-treated animals. (A) Paraffin-embedded kidney sections were used, and oxidative stress was assessed with marker protein 8-hydroxyguanosine. Control and nHNK groups showed minimal amounts of 8-OHdG, an intense signal can be detected in the cisplatin-injured animals, and signal intensity was decreased in the treatment group. (B) To assess the antioxidant capacity of the kidney, total antioxidant capacity (TAC) assay was carried out. Cisplatin-injured kidney showed the lowest total mitochondria enzyme activity as assessed by TAC assay (red line). Groups in the presence of nHNK (blue and green lines) showed the highest two recording optical density values, which indicated that more active mitochondria enzymes were available in these groups, which suggested that nHNK maintained and facilitated the antioxidation property of the kidney. (C) Western-blotting analysis showed the majority of the cytochrome c protein appeared in the mitochondria fraction (M) of control, nHNK alone and the treatment groups with minimal detection in the cytosolic fraction (C). However, a significant reduction of total cytochrome c protein expression in the mitochondria fraction was observed in cisplatin-injured animals.