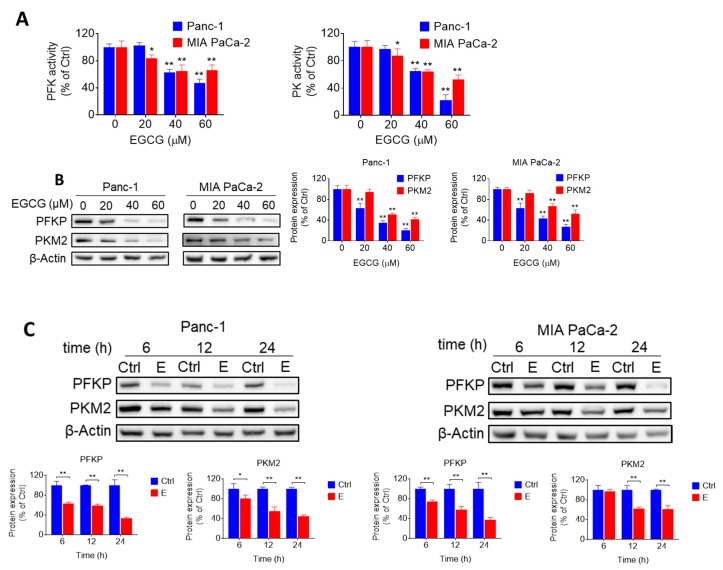
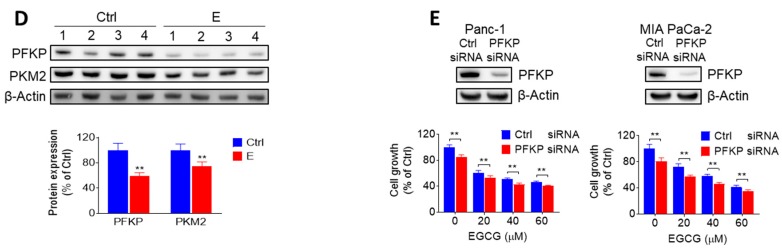
Figure 2.
EGCG inhibits glycolysis through suppressing rate-limiting enzyme activity and expression. (A) Phosphofructokinase (PFK) and pyruvate kinase (PK) activities were determined in Panc-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells after treatment with EGCG for 24 h. Results are expressed as a percentage of control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (B) Immunoblots for platelet-type phosphofructokinase (PFKP) and pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) in total cell protein extracts from Panc-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with escalating concentrations of EGCG, as indicated, for 24 h. Loading control: β-Actin. Bands were quantified and results are expressed as a percentage of control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (C) EGCG (40 µM) inhibited PFKP and PKM2 protein expression in a time-dependent manner in Panc-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells. Results are expressed as percentage of control and presented as the mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p <0.01 vs. control. (D) Immunoblots of PFKP, PKM2 expression on tumor tissue from control- and EGCG-treated (10mg/kg/d) mice. Results are expressed as a percentage of control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. control. (E) Effect of silencing PFKP on EGCG-induced cell growth reduction. Panc-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells were transfected with either control or PFKP siRNA. After transfection, cells were treated with EGCG for 72 h and cell growth was evaluated. Results are expressed as percentage of control; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. control. Immunoblots to verify PFKP silencing were performed on whole cell extracts obtained from these cells (top panel).