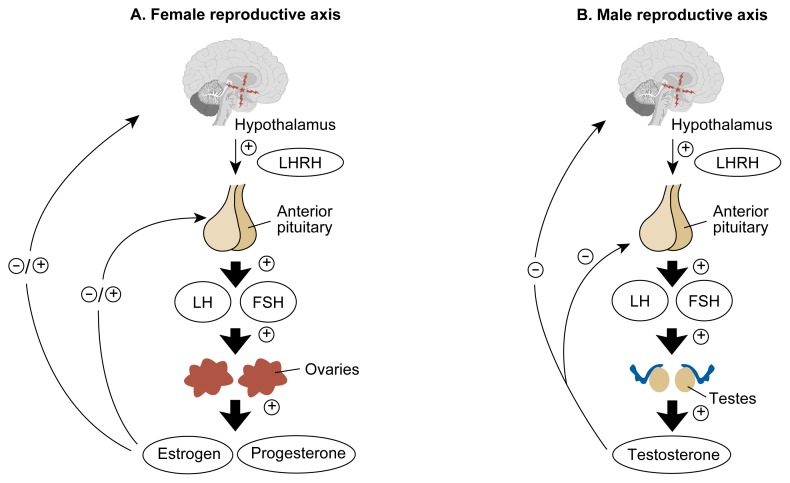
Figure 2.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in males and females. The hypothalamus secretes luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH), which controls the anterior pituitary gland’s secretion of both follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). In the female reproductive axis (A), these two gonadotropic hormones stimulate the ovaries to secrete estrogen and progesterone, which circulate back to the hypothalamic-pituitary unit and either inhibit or excite the production of FSH, LH, and LHRH. In the male reproductive axis (B), the gonadotropic hormones stimulate production of testosterone by the testes; testosterone also feeds back to the hypothalamus and pituitary to inhibit production of LHRH and the pituitary gonadotropins.
⊕ = excites
⊝ = inhibits