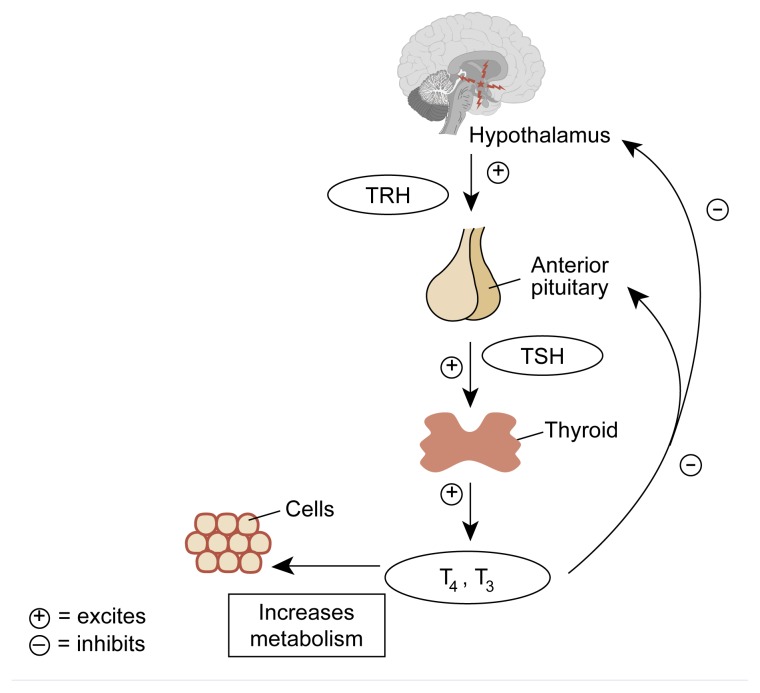
Figure 5.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. The hypothalamus produces and secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating cells of the anterior pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then stimulates secretion of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) by the thyroid gland, the primary effect of which is to regulate cell metabolism. T4 and T3 both feed back to the hypothalamus and the pituitary to reduce TRH and TSH secretion.
SOURCE: Guyton, A.C. Human Physiology and Mechanisms of Disease. 5th ed. Philadephia: W.B. Saunders, 1992. pp. 566–568.